Import tariffs are one of the oldest tools in the protectionist’s toolkit, used for centuries to shield domestic industries from unfair foreign competition. In the modern world, however, tariffs have become an economic weapon in trade wars between nations to inflict pain on each other’s economies. The most notable example is the tit-for-tat tariff battle between China and the United States. And as China is one of the largest exporters to the USA, with Chinese goods totaling $577.13 billion in 2021, the repercussions will be detrimental to the global economy.
But what caused this trade dispute? What will be the impact on the U.S. economy? And how can wholesalers and retailers manage the tariff-associated costs in their business operations? Well, it’s time to take a sip of coffee and read this blog to get a comprehensive overview of the current trade war between the USA and China.
Table of Contents
What are “China Tariffs”?
What’s the impact of China Tariffs on the U.S. economy?
What’s the impact of China Tariffs on U.S. businesses?
Free trade is the key to greater prosperity
What are “China Tariffs”?
The precursors of the trade war

The first flames of the trade war between China and the United States were ignited when the Trump administration initiated a Section 301 investigation into China’s unfair trade practices. The resulting inspection report, conducted by the United States Trade Representative (USTR), concluded that China uses a range of tools to acquire U.S. sensitive technologies through forced technology transfers, intellectual property theft, and discriminatory licensing restrictions.
In March 2018, President Trump’s administration imposed over $50 billion worth of tariffs on Chinese goods. China responded with its retaliatory action against the U.S., imposing tariffs on billions of dollars worth of American exports. The retaliatory tariffs led to a back-and-forth battle between the two countries, negatively affecting both U.S. consumers and businesses.
The affected Chinese imports

The proposed tariffs were published under 4 lists and focused on items that were deemed unfairly subsidized by the Chinese government, including industries such as aerospace, robotics, and machinery. Lists 1 and 2 were aimed at non-consumer products such as industrial and medical products. They imposed tariffs of 25% on about $50 billion worth of Chinese imports.
And as China failed to make concessions in the trade negotiations, a third list imposed 10% tariffs on additional Chinese goods, with a total import value of $200 billion. The tariffs went into effect on September 24 of 2018 and were increased to 25% in May 2019. And on September 1 of 2019, the U.S. administration announced the fourth list of tariffs against China. This final set of tariffs on Chinese goods was broken down into two lists: 4A and 4B. As of February 14 of 2020, list 4A goods were subject to a 7.5% additional tariff, but list 4B has never been put into effect.
How the Biden administration is addressing China Tariffs

When Joe Biden took office in January 2021, he inherited a trade war that was already in progress. The new US administration was expected to remove tariffs and work toward a more open trading relationship with their biggest international partners, including China. But Biden’s administration has been moving very slowly on this issue, and have left most of Trump’s tariffs in place.
The reason behind this cautious and skeptical stance is the failure of China to meet the Phase One commitments, which came into effect in February 2020 and were made as part of the US-China comprehensive economic dialogue. In exchange for removing the imposed tariffs, China was supposed to increase its purchases of US goods and agricultural products by $200 billion.
Although American business leaders have been pressuring the US government to remove these tariffs for months now (and even threatening to move production overseas), it seems unlikely that Biden will take any steps toward trying to undo what Trump has done so far—or even lowering them significantly.
What’s the impact of China Tariffs on the U.S. Economy?
A measure that backfired on the U.S. economy
The Trump administration intended to improve the U.S. annual trade deficit of $500 billion by pushing its current account balance toward surplus, but in reality, it fell deeper into deficit. On the other hand, China’s current account balance increased by +0.4% between 2018 and 2020, and the first quarter of 2022 alone saw China register a surplus of $89.5 billion.
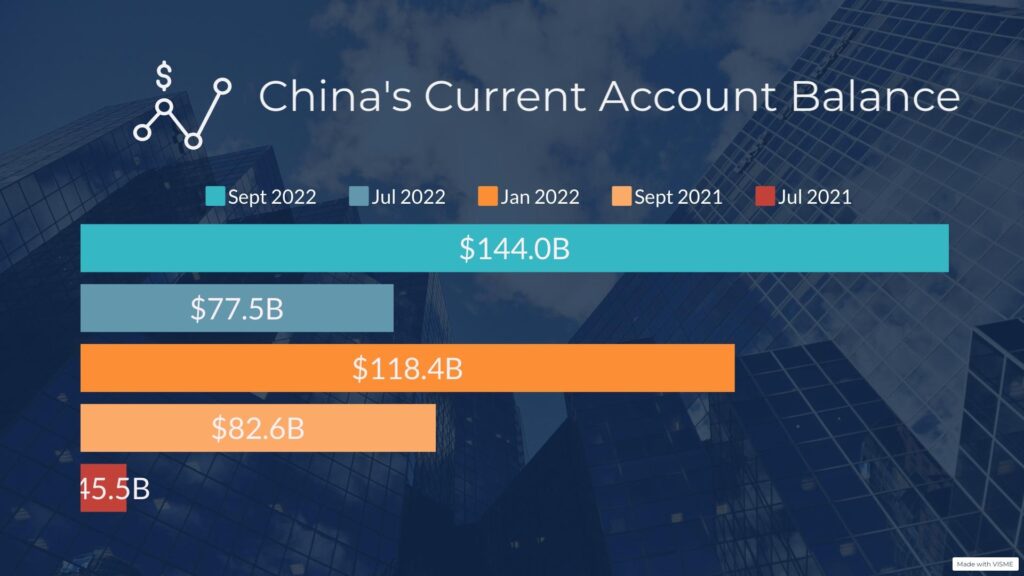
The reason China’s trade imbalance with the United States continued to grow is partly due to the imposed retaliatory tariffs on U.S. goods and commodities. This retaliation has affected the export competitiveness of US companies, resulting in a decline in overall trade balance growth. Moreover, tariffs have little influence on trade balances; they are only one factor in a complex equation that includes other macroeconomic factors like population growth, fiscal policy, and exchange rates.
Customers are the ones who bear the burden of tariffs

Tariffs are a tax on consumers as they directly impact their wallets and result in overall higher prices. According to a paper published by the Tax Foundation, tariffs imposed by the Trump administration have hurt the U.S. agriculture industry and could inflate food prices in the long run. The retaliatory tariffs set by China reduced U.S. agricultural exports by $27 billion, with soybean exports taking the biggest drop by 71%.
This cause-and-effect relationship between tariffs and inflation is evident; when businesses are forced to pay higher for their imported goods, they pass those costs onto final consumers. This is just one example of how protectionist trade policies can hurt an economy. Tariffs also disincentivize innovation and encourage companies to stay within their comfort zone instead of pushing themselves to create new products for new markets or improve existing ones.
Tariffs are anti-liberalization measures
Tariffs are a reversal of free trade policies. They prevent the free flow of goods and services, which is the cornerstone of global economic development. They lead to slow economic recovery and create uncertain global financial markets. This in turn will result in higher interest rates and make it difficult for businesses to invest in expansion or hire more people.
Bilateral trade agreements are on the rise

In recent years, many countries have been trying to offset the negative impacts of trade globalization through multilateral preferential trade agreements. But these agreements are difficult to negotiate and take a long time to conclude. The negotiating process is complicated by the fact that different countries have different interests and priorities. Moreover, multilateral agreements may require ratification by each country’s legislature, which can be a lengthy process.
On the other hand, bilateral trade agreements can be concluded much more quickly because they focus on only two countries’ interests and needs at a time. Moreover, they allow countries to protect their infant industries from foreign competition while still having access to the markets and resources of partner countries. This allows countries to focus on their strengths while also protecting each other’s interests.
What’s the impact of China Tariffs on U.S. businesses?

Who pays the imposed tariffs?
The misconception that China is paying tariffs on their exports to the USA is understandable, but it doesn’t accurately reflect how tariffs work in practice. When a U.S. company imports goods from China, it pays taxes and duties to the U.S. government for those goods based on their value, and most of these customs tariffs are then passed along to the consumer through higher prices at retail stores and online retailers like Amazon or Walmart.
To understand how import tariffs are calculated and their impact on the final consumers, let’s take the example of a U.S. agricultural machinery retailer that imports two-wheel tractors from China. Let’s assume that this retailer purchased 50 tractors for $3,000 each from a Chinese manufacturer. After applying the 25% import tariff on this transaction, the retailer will pay $3,750 per tractor instead of $3,000. The extra $750 is paid as import duties to the US government.
How do businesses manage tariff costs?
When faced with the cost of tariffs, passing them on to customers is not the only option. Businesses can mitigate tariff risks using some of the following techniques:
Nearshoring
U.S. businesses can reduce their tariff impacts by moving production to countries not subject to U.S. tariff actions such as India, Vietnam, and Malaysia. While these countries may not have the same level of quality control that China’s factories offer, their products can still prove competitive and cost-effective.
Absorbing the costs
Certain businesses try to figure out how to absorb the extra costs and keep their products affordable for consumers. This can be as simple as changing the materials used in manufacturing or as complex as redesigning an entire product line. For example, switching from synthetic plastic to domestically-produced biodegradable plastic.
Free trade is the key to greater prosperity
While tariffs may seem like an effective way of protecting local sectors and imposing political policies on trading partners, they end up hurting lower-income consumers by raising prices on many everyday goods and services. Trade protectionism will only lead to higher costs for consumers, less competition in domestic industries, reduced access to foreign markets, and lower economic growth.
It’s time for countries around the world to embrace free trade and globalization to create a more integrated global economy, which will in turn lead to greater prosperity for all people. Stay up-to-date on the latest news about global logistics and trade by visiting Alibaba.com’s blog center!

Looking for a logistics solution with competitive pricing, full visibility, and readily accessible customer support? Check out the Alibaba.com Logistics Marketplace today.




