It is important to get your shipping documentation right when shipping your goods internationally. You want the shipment to move from origin to destination smoothly and without any delays. Any errors or omissions in any of the shipping documents can hold up your shipment unnecessarily.
This article explains the key shipping documents that you will need, and what purpose each of those documents serves.
Table of Contents
The importance of shipment documents
Product information requirements
Types of contract of carriage
Final thoughts on shipping documents
The importance of shipment documents
Shipping documentation provides the information to be used by the exporting country’s customs authority, the carrier(s) that transport the shipment, and the importing country’s customs authority. Documentation falls into four key areas:
- information about the products being shipped
- the legal contract of carriage between all parties
- the declarations and licenses required for export
- the declarations and licenses required for import
Shipping documents for product information
Product information is important for each party involved with the shipment, to know what is being shipped, what the terms of sale and purchase were, and whether the goods need special care, or approvals and licenses. Shipping documents which provide this product information include:
- commercial invoice
- packing list
- certificate of origin
- inspection certificate
Additional shipping documentation
Other types of documents may be required depending on the nature of the commodity. For example, items that may be considered hazardous may require a dangerous goods form or material safety data sheets.
Contract of Carriage
A Contract of Carriage is an agreed contract between the shipper and the carrier for the transportation of the goods. The Contract of Carriage sets forth the terms, conditions, obligations, liabilities and responsibilities of each party with respect to the carriage of the goods. A Bill of Lading is used for ocean carriers and an Air Waybill for air freight carriers.
Declarations and licenses required for export
The export customs authority may require your shipment to have one or more export licenses before allowing your goods to be exported. Most countries typically control the types of items that can be exported from their country, to protect their own industry and culture. They may also control what items can be sent to the destination country, and determine the use of these items and the quantities that can be exported.
The required export licenses will depend on the type of products, nature of the transaction, and destination country. Additional export documentation may be required.
Declarations and licenses required for import
The import customs authority may require your shipment to have one or more import licenses to permit your goods to be imported. Countries control what types of items can be imported into their country in the same ways as countries control what can be exported.
There are different types of import licenses required by the import customs authority and there may be a number of different government departments involved in approvals.
Product information requirements
Commercial Invoice
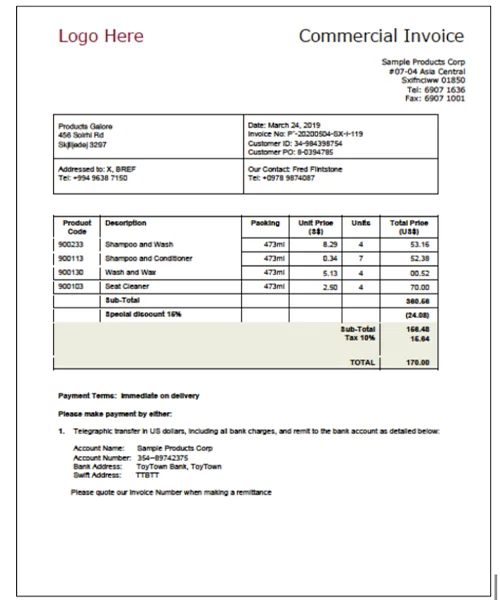
The commercial invoice is a legal document between the seller (exporter) and the buyer (importer) that details the goods being sold and the amount the customer is to pay. It is the invoice for the goods issued by the seller to the buyer. The commercial invoice is one of the key documents that customs uses to determine the value of the goods and therefore the customs duties.
The declared value is the purchase price between buyer and seller, not the price of the goods when sold in the destination market.
Packing List
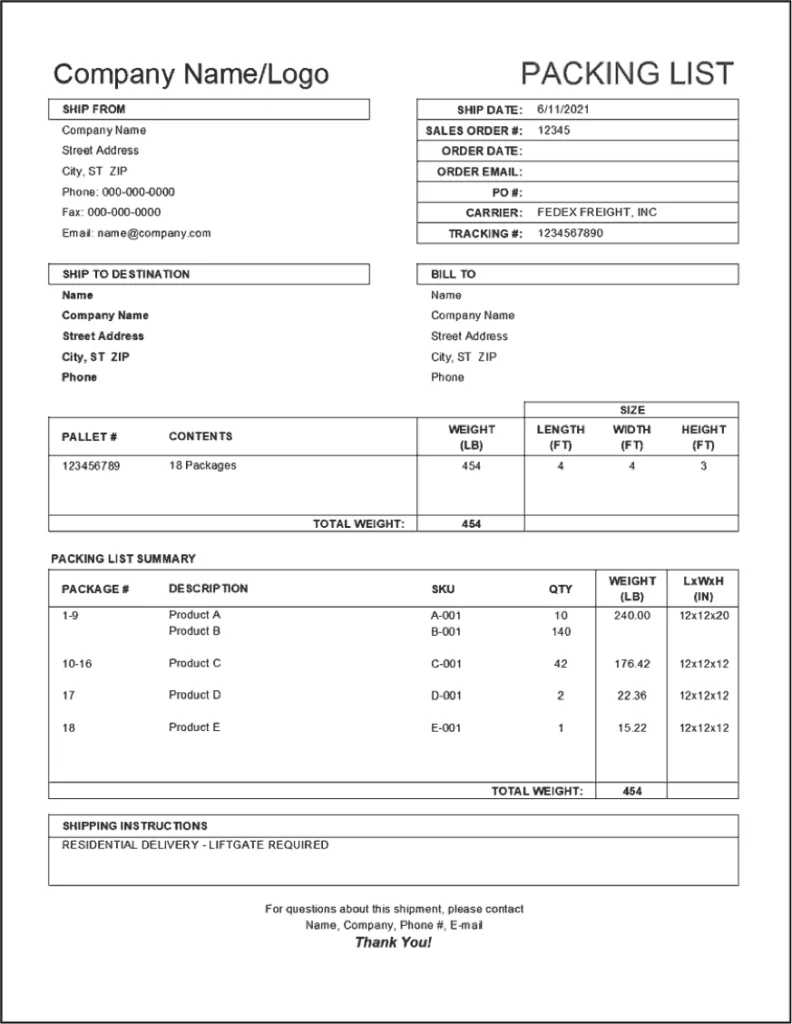
Freight forwarders, carriers and customs officials all use the packing list to check against the physical cargo and to book shipping space. A packing list details the contents of the shipment, and the packaging including type (e.g. box, crate, drum), number of packages, and total weight.
Certificate of Origin
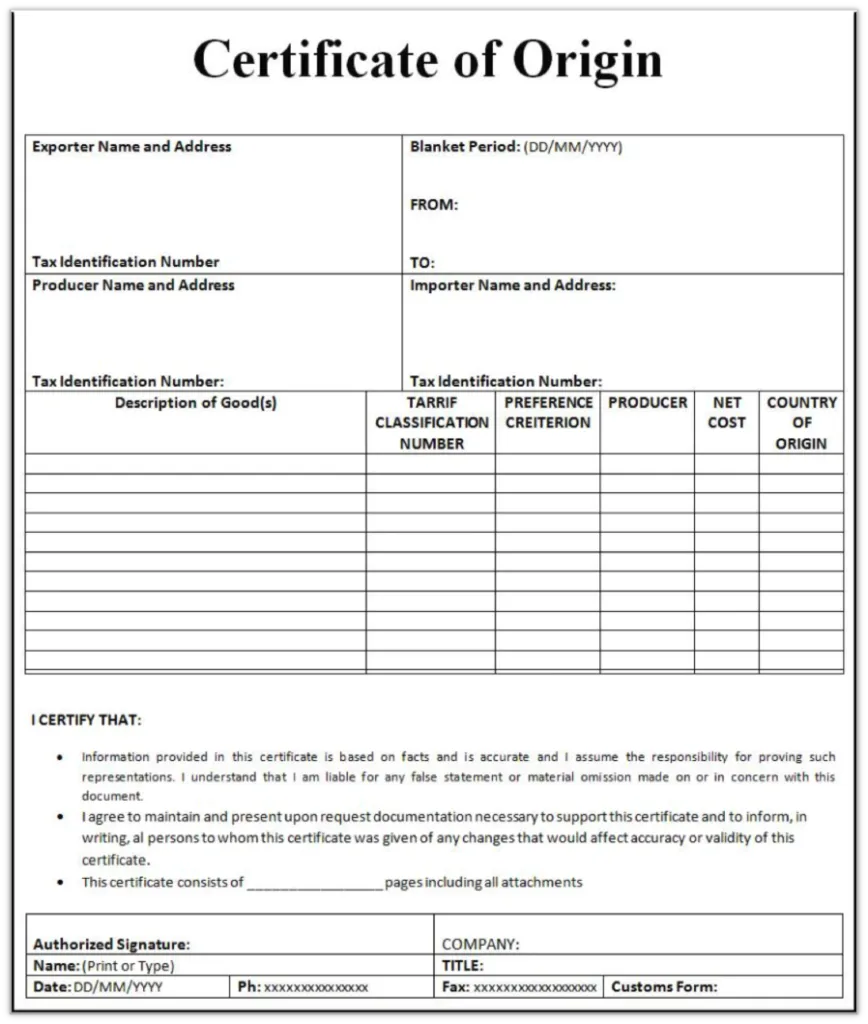
Some importing countries require a certificate of origin to identify where the goods were originally manufactured, and this may be required even if this information was included on the commercial invoice. Importing countries may have restrictions on import from certain countries or apply additional tariffs, so it is important that the true origin country is properly declared.
Inspection Certificate

An Inspection Certificate states that the goods in the shipment have been inspected by a competent authority, and conform to the terms and specifications stated in the sales contract.
- an Official Inspection Certificate is used by customs authorities to check and confirm whether the goods in the shipment are as described in the commercial invoice
- a Commercial Inspection Certificate is completed for the buyer before shipping to determine if the manufactured goods adhere to the terms of the sales contract, and to meet the agreed manufacturing quality and other contract specifications
Types of contract of carriage
Bill of Lading
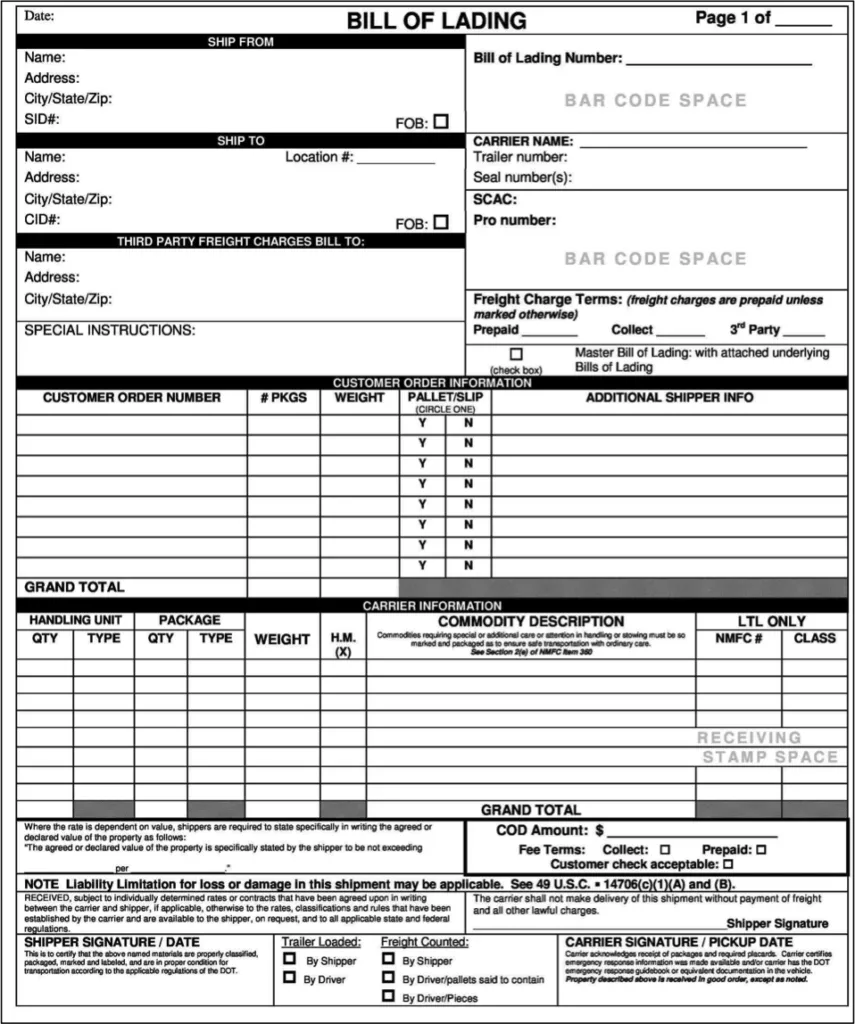
A Bill of Lading (BOL) is evidence of a contract of carriage, used for ocean freight, between the owner of the goods and the carrier. It serves three main functions:
- as receipt and acknowledgement that the goods have been loaded
- as evidence and terms of contract of carriage
- as a transferable title to the goods
The 3 types of Bills of Lading and their uses
Original Bill of Lading (OBL)
The Original Bill of Lading (OBL) is a legally binding contract of carriage. It is a hard copy document, completed by the carrier, and then provided to the shipper once the cargo is confirmed on board the vessel. The shipper holds the original Bill of Lading until they receive payment from the importer. The shipper then sends the original documents to the importer at the final destination (usually by courier).
The importer must surrender an endorsed original Bill of Lading to the carrier for the shipment to be released.
Express Bill Of Lading
An Express Bill Of Lading is used when the carrier delivers the goods to the importer without any original Bills of Lading being issued, and is a way to move a shipment forward quickly (expressly) without the legal documentation that binds the shipper and importer on matters such as payment, delivery and title of goods. It is commonly used when the importer has a long-standing payment relationship or has prepaid the shipper for the goods.
House Bill of Lading (HBL)
The House Bill of Lading (HBL) is produced by the freight forwarder and is issued to the supplier once the cargo has been received. It is the formal acknowledgment of the receipt of goods being shipped by the freight forwarder.
Air Waybill (AWB)
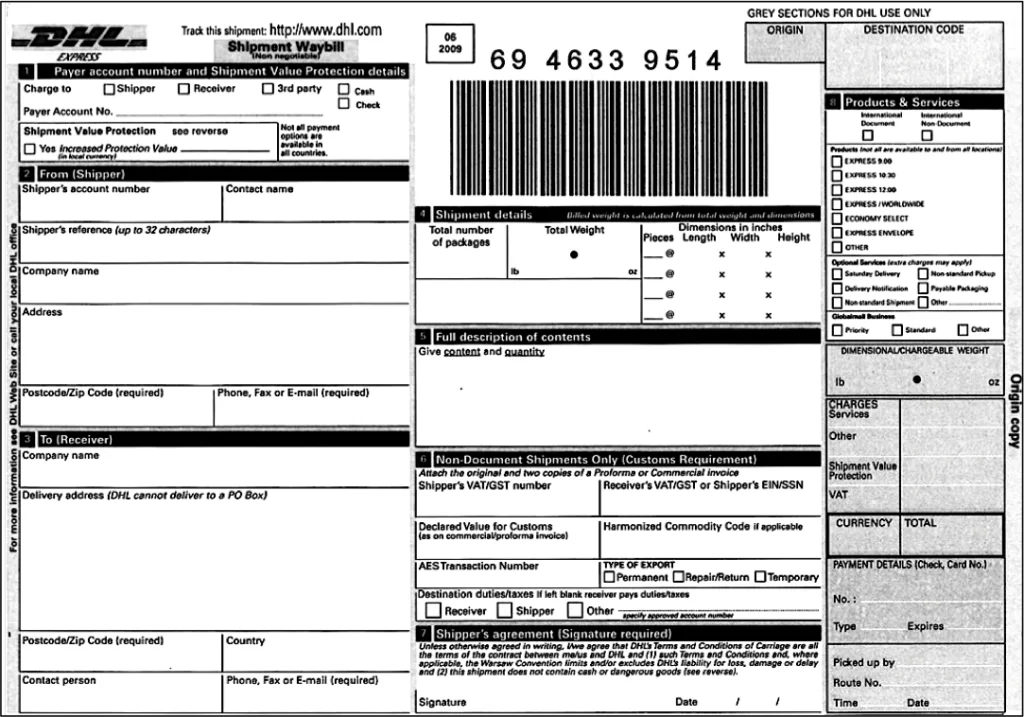
Air freight shipments require Air Waybills, instead of Bills of Lading, but serve the same purpose of legal contract of carriage between parties. An Air Waybill is attached to, and accompanies, goods shipped by an international air carrier. The document provides detailed information about the shipment and allows it to be tracked in transit. Air Waybills are shipper-specific and are not negotiable documents or transferable, and do not confer title.
Types of Air Waybill
House Airway Bill (HAWB)
The House Airway Bill (HAWB) is produced by the air freight forwarder or air express company and a copy is given to the shipper on pick up as a receipt.
Master Airway Bill (MAWB)
The Master Airway Bill (MAWB) is produced by the airline and provided to the air freight forwarder or air express company.
Final thoughts on shipping documents
Shipping cargo internationally can be a smooth process provided that shipment documentation requirements are met.
For shipping, whether by air or sea, complete product information must be provided, including a contract of carriage (whether Bill of Lading or Air Waybill), and any necessary inspection certificates and licenses.
For customs export and import, these shipping documents are equally important, but there may be additional requirements for specific licenses and compliance documents that must be completed.

Looking for a logistics solution with competitive pricing, full visibility, and readily accessible customer support? Check out the Alibaba.com Logistics Marketplace today.