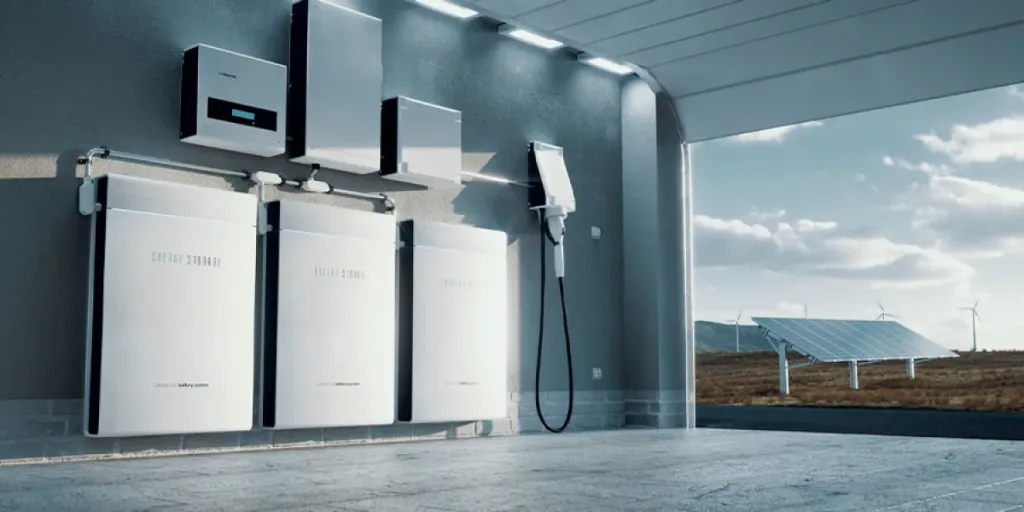
Most solar-powered houses have a grid tied solar system. However, off-grid solar systems have become more popular due to the increased energy autonomy they offer users. A key piece of equipment associated with these systems is the off-grid solar inverter.
In this article, we will explore how off-grid solar inverters work in comparison to inverters used for hybrid on-grid systems. The article will also analyze the global off-grid solar market, looking at the current market size, key market drivers, and projected growth. It will then offer a buying guide with key factors to consider when choosing the best off-grid solar inverter.
Table of Contents
How do off-grid solar inverters work?
Overview of the global off-grid solar market
5 factors to consider when choosing the best off-grid solar inverter
Choose the best off-grid solar inverter
How do off-grid solar inverters work?
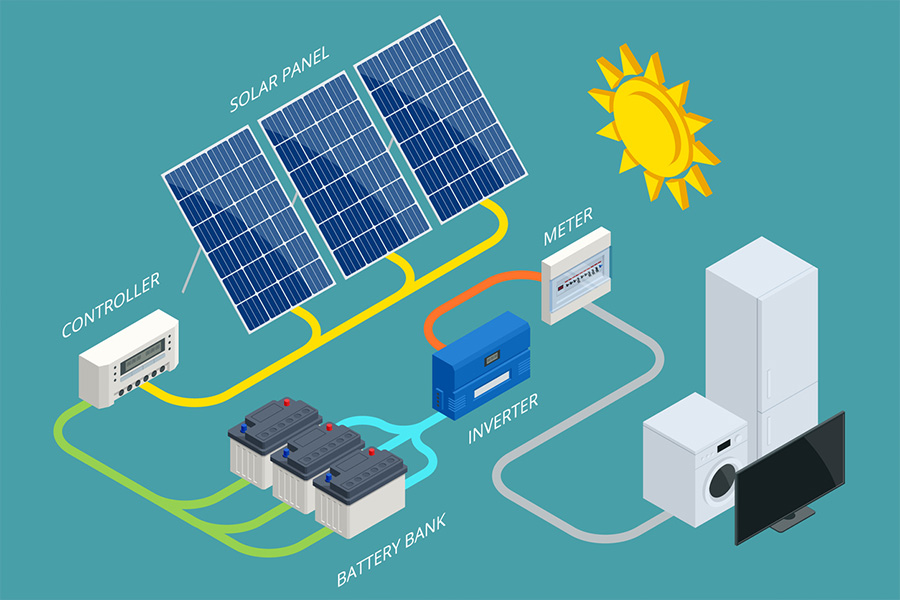
The two main types of solar powered systems are those that are connected to the grid (hybrid or on-grid) and those that are disconnected from the grid (off-grid). While both use the same power source of energy collected from the sun through solar panels, they store and utilize excess energy differently.
With a hybrid solar system, excess electricity is sent to the power grid, while solar off-grid inverters use battery banks that store the DC solar power fed into them by the off-grid solar panels. That power is then converted by the inverter into the AC power that is used to power home appliances.
Off-grid solar systems are far more complicated compared to hybrid systems as they require additional components such as battery monitors, charge controllers, and DC and AC circuit breakers.
Overview of the global off-grid solar market
A Vantage Market Research’s 2022 report shows that the global solar inverter market at large is projected to reach a market value of US$ 12.93 billion by the end of 2028. The market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% from its 2021 market value of US$ 7.92 billion.
When it comes to the off-grid solar market specifically, Vantage predicts market growth at a CAGR of 11%, with the market growing from a value of US$ 2.8 billion in 2020 to US$ 6.45 billion by 2028.
The looming energy crisis, fluctuating oil prices, and increased international agreements promoting sustainable development schemes are considered key drivers of growth within the market of solar power inverters.
5 factors to consider when choosing the best off-grid solar inverter
1. Output voltage
One of the first things to consider when selecting an off-grid solar inverter is determining the load requirements. This is usually the same as the standard supply voltage or load nominal voltage of a certain area.
Doing a load analysis helps retailers find out what voltages their customers will require. Output voltage for Europe and Africa is 240V, while it is 120V in the US. Most residential applications require 110/220 VAC, which is the voltage requirement for AC household loads.
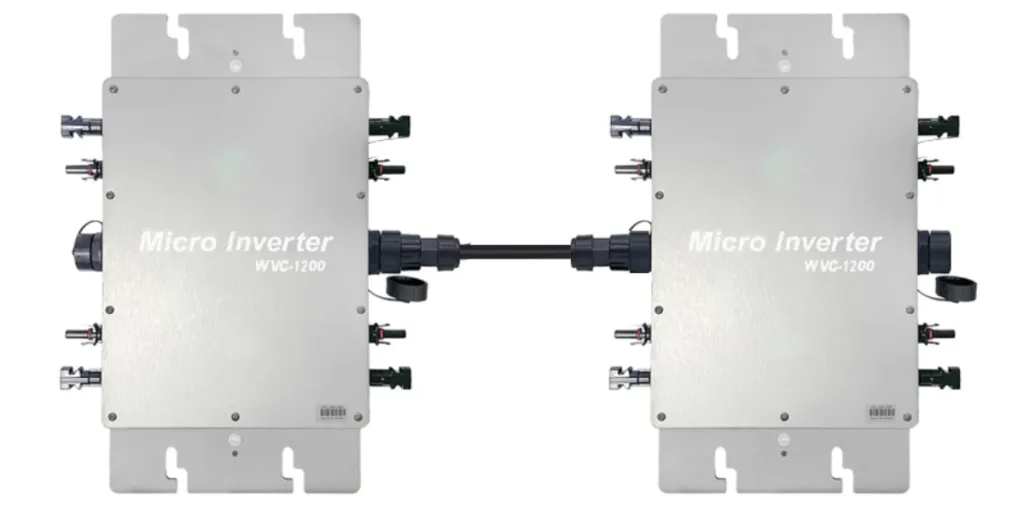
To get a higher output voltage, users can use “inverter stacking,” which involves using multiple inverters in series. As long as the solar inverters used are compatible, a residential user would be able to connect two 120 VAC inverters to double the output voltage to 240 VAC.
2. Power range

The next factor to consider when choosing the best off-grid solar inverter is the power range that the inverter comes with. Ultimately, the equipment being chosen should be able to meet the user’s power needs or handle their load.
Below is a list of various inverter power ranges and their typical applications:
- 1–2 kW: TV, fridge, phone, small cabin with lights
- 2–4 kW: Small energy-efficient homes, larger cabins
- 4–8 kW: Most off-grid homes
- 8–16 kW: Larger off-grid homes, small businesses, farms, or ranches
The most popular power range is 4–8 kW as it can meet most common household power needs.
Depending on the target customer, it is important to also consider future loads that may require power. This means that the off-grid inverters installed should typically be able to handle any growth in power needs over the next few years. Hence, a system targeted toward retired couples should be different from that targeted toward young families.
3. DC input voltage

Once the power capacity of the off-grid solar inverter is established, it will now be time to consider the DC input voltage range of the equipment. This can be established by looking at the inverter’s specifications or spec sheet.
The input DC voltage is used to determine the nominal battery voltage that matches the inverter. As a rule, the maximum PV DC output voltage should not exceed the maximum DC input voltage listed in the inverter’s specs.
4. Battery capacity

The next factor to consider in the off-grid solar power systems selection process is the battery size that will be required. The retailer will have to determine if the customer being targeted would typically require energy storage that covers usage for just one day or a system that has extra backup capacity.
To ensure accuracy during this process, it is important to take into account a number of variables related to the battery. These include the battery type and its chemistry, round-trip efficiency, maximum depth of discharge (DoD), maximum charge rate, and days of autonomy.
The general rule for solar battery backup is to aim for storage that covers at least 2–3 days of usage during the year’s highest-usage time.
5. Built-in solar charge controller

Off-grid solar inverters come with built-in solar charge controllers that regulate the power coming from the solar panels and transferred to the batteries. There are two types of charge controllers typically used for off-grid solar inverters: Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controllers and Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) controllers.
MPPT controllers are considered technically better as they can convert higher solar panel voltage to lower voltage and are able to charge batteries with lower power losses or higher efficiency. MPPT can deliver 93–97% efficiency in their power conversion; however, they are more costly compared to PWM controllers.
PWM controllers are cheaper, but they can cause up to 60% of power loss. This makes them unideal for large systems but a viable option for smaller systems. Ideally, it is best to select an inverter with a built-in charge controller that optimizes voltage transfer so that the battery bank receives the maximum amount of energy.
Choose the best off-grid solar inverter
Selecting the best off-grid solar inverter for target customers requires careful consideration of a number of factors, including output voltage, power range, DC input voltage, battery capacity, and built-in solar charge controllers.
All these factors have a bearing on the type of off grid solar power system that users have, so retailers must consider who is being targeted as this will help to establish the most optimal inverter option for them.
Ultimately, customers are looking for systems that are easy to maintain, simple to use, and hassle-free. Accurately calculating the electrical loads and usage patterns of prospective customers enables correct sizing of the off-grid solar system, higher functionality, and minimal system failure.




