Every seller’s goal is to sell more products and reach new buyers. But how is this possible? One way to do so is through creating a buyer persona. The buyer persona tells businesses about their target audience. It helps them to find the goals, pain points, and interests of their audience.
This means businesses can use a buyer persona to keep their marketing efforts focused on their specific targeted audience. So read on to find out what a buyer persona is, how to create a buyer persona, and tools for creating a buyer persona such as a buyer persona template.
Table of Contents
What is a buyer’s persona?
How to create a buyer persona?
Example of a buyer persona
Tools for creating a buyer persona
Conclusion
What is a buyer’s persona?
A buyer persona is also known as a marketing persona, customer persona, and audience persona. A buyer persona is a semi-fictional representation of a business’s targeted customers.
It contains information like customers’ demographics, pain points, goals, interests, and motivation and it helps a business to better understand its audience’s needs, aims, hardships, and buying patterns. Businesses use buyer personas to make important marketing strategies like what their message should be and what marketing channels they should use to target their customer.
Hence it will improve a business’s brand awareness, engagement, conversions, and sales. The buyer persona is created by research and data on customers. It is a common practice to create 3 to 5 buyer personas to represent different groups of customers.
How to create a buyer persona?
Here is a step-by-step method to create a buyer persona:
Step 1: Questions to ask

Before starting the research, first, a business must define what they want to know most about their customers. A good approach is to write questions. These questions are the basis of effective research. Every business can add more questions according to their needs.
Here are some questions a business should include in research:
| Personal questions |
| The customer’s age |
| Gender |
| Location |
| Education level |
| Social media channels they use |
| Influencers they follow |
| Publications they trust |
| Content they post and share |
| Questions or topics they talk about |
| Industry-specific questions |
| Occupation |
| Job title |
| Career goal |
| Challenges in the workspace, such as cost, quality, logistics service, payment, and technology |
| How do they prefer to communicate in the workplace? |
| Product-related questions |
| Did they ever use your product or any similar products? |
| How do they choose suppliers for their business? |
| What are the factors involved in making buying decisions? |
| How has your product solved their problem and what attracted them to it? |
| What are the problems they faced using your product? |
| How have your competitors’ products solved their problems and what attracted them to your competitors’ products? |
| What are the problems they faced using your competitors’ products? |
| How do they like to interact with suppliers? |
Step 2: Conduct customer research

Conducting customer research is the core of creating a buyer persona. Brands should research their existing customers, previous customers, and leads.
Research must divide into different sections like interviews, surveys, and online data. Businesses should collect information from every department that interacts with customers: spanning marketing, sales, and customer relations. This is the best way to get information about customers.
Here is a roadmap to conduct research:
Interview internal staff

If a business is already selling products they should create a buyer persona from their current clients. Their different departments have unique information about their targeted audience.
Information from different departments can be obtained in the following ways.
Sales team:
The sales team know about:
- Types of customers they meet
- Factors that make or break the deal
- Most and least favorite products
- How do they order the products?
- Unique selling points that are helpful to their ideal client
- Reasons customers prefer yours brand over competitors
Marketing team
The marketing team can share insights about
- The onboarding process
- The best content that brings clients to their website
Customer service team
The customer service team know about:
- Most common questions by leads
- Frequently asked questions by current clients
- What skills do their customers need to use their products?
- Most common objections to products
Direct conversations with clients

Getting information from internal teams is a start to understanding customers. But to know more about customers it’s good to directly interact with them.
After collecting information from internal teams, businesses should validate this information from direct conversations with their clients. In fact, they should focus on their ideal client, based on their existing best clients.
- Which ones pay them most?
- Which ones are the easiest to work with?
- Which ones have the best results?
- Which refer them to new clients?
It’s sometimes hard to communicate directly with clients so businesses should give them some incentives for giving their time. Incentives can be free shipping and discounts on future orders.
The best ways to directly interact with clients are:
- Surveys
- Interviews
Online data

The last part of research is gathering online data for crafting a buyer persona.
These are the best sources to find online data about customers.
Google Analytics

Google Analytics is a free tool to check online behaviors of the ideal customers.
Some cool metrics sellers can find about customers on Google analytics are
- Language
- Location
- Gender
- Browser
- How they find you
- Whether they are a new user or an old one
Social listening

Another great way to learn about the ideal audience is to keep an eye on their social media activities. It is already mentioned in the question sections what businesses should check about their audience’s social media activities.
Moreover, FB analytics is an amazing tool to find insights about the targeted audience. A brand should also check Reddit and Quora to find questions people are asking about their industry and products.
How do you do research if you have no customers?
If a business is new and has no customers then it should check competitors’ customers. Go to their blogs and social media channels and check the profiles of the audience interacting with their content.
Similar web, BuzzSumo, and Semrush are good tools to conduct customer research.
Step 3: Segment the customer

After collecting all data, the next step is to analyze the data to make relevant groups. When analyzing data, sellers will notice some similarities.
They will find customers with the same age, demographics, job titles, industries, goals, and pain points. They should divide these customers into groups.
The seller can make groups according to industry or job title. This will help them to decide the number of buyer personas they need to create.
For example, the seller, who operates a B2B textile company has decided to make groups of his ideal clients according to their industry sizes. After grouping his customers according to their size he noticed he had three types of customers.
- Small to midsize clothing companies with a staff of 3-20 people and with the purchasing decision made by their owners.
- Mid-size companies focused on women’s clothing and typically with 50-100 people on staff. Their purchasing decisions are usually made by the procurement director.
- Large-size clothing brands that have many factories in different countries. Their decisions are made by the procurement manager when the order value is lower than US $50k.
So the seller has decided to create three buyer personas for these customers as their motivations, needs, goals, and pain points are different from each other.
Step 4: Create a buyer persona

Once a business has completed research and segmented the customers, they are ready to create a buyer persona. They should give the buyer persona a name, stock photo, and other identifying characteristics. A buyer persona should seem like a real person.
First, they must decide what main elements they want to add to their buyer persona. Here are some basics elements to add to a buyer persona
Basic elements for client A
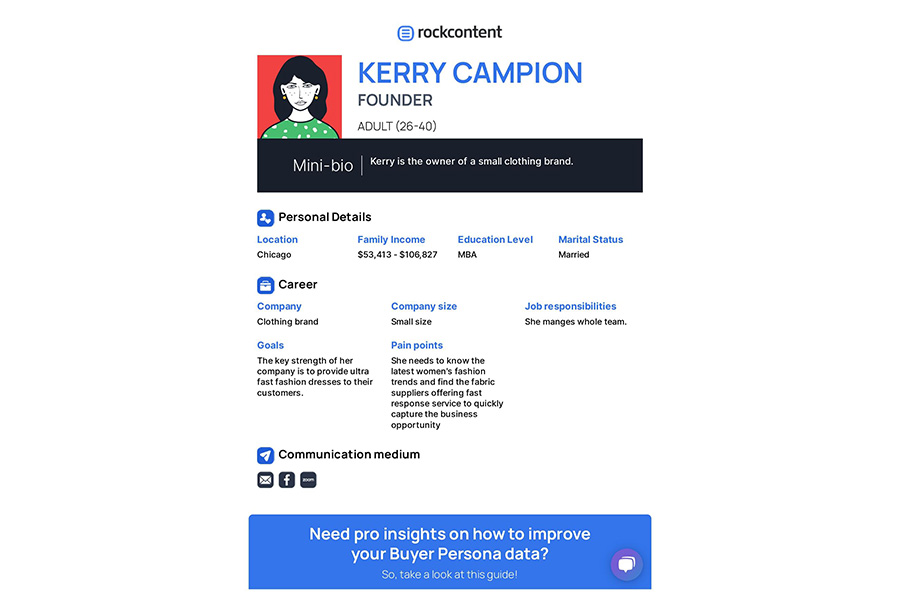
Fictional name: Kerry Campion
Stock photo
Personal data: She is 30 years old, lives in Chicago, and has an MBA.
Role at work: She is the owner of a small clothing brand.
Social media use: She uses Instagram, Facebook, and Tik Tok for professional use. Her favorite form of content is pictures of trending clothes designs.
Work-related issues: The key strength of her company is to provide ultra-fast fashion dresses to their customers. She needs to know the latest women’s fashion trends and find fabric suppliers offering fast response service to quickly capture business opportunities.
Basic elements for client B
Fictional name: Mark Jefferson
Stock photo
Personal data: He is 37 years old, and lives in New York City.
Role at work: He is the procurement director of a mid-size clothing brand.
Social media use: He uses Google for professional use. His favorite content is fabric price trend analysis and global logistics news.
Work-related issues:
The input cost of his company is high and he wants to reduce it. He needs good suppliers that provide quality fabric at minimum costs. Local suppliers are expensive. International suppliers are providing fabric at low cost but he is worried about quality and shipping issues.
Basic elements for client C
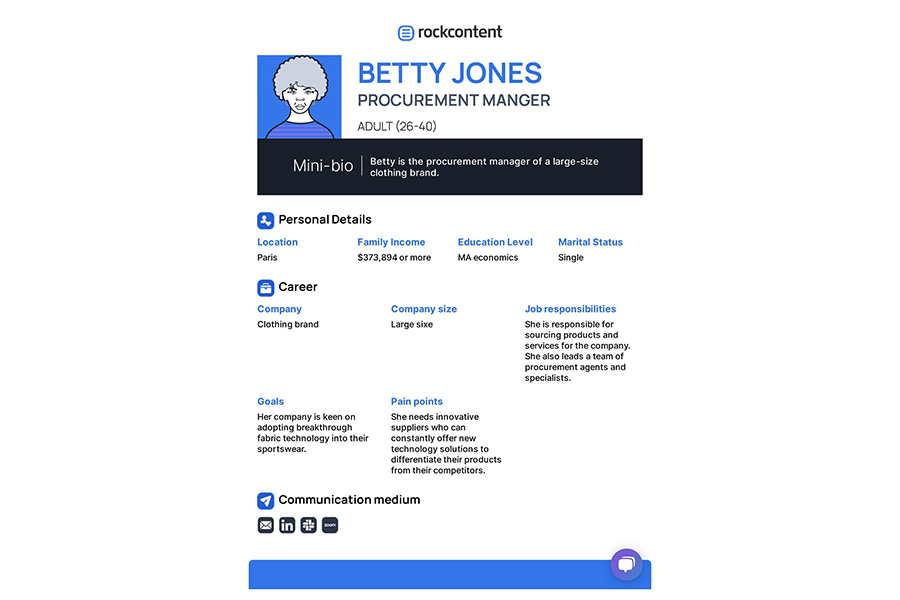
Fictional name: Betty Jones
Stock photo
Personal data: She is 40 years old, and lives in Paris.
Role at work: She is the procurement manager of a large-size clothing brand specializing in sportswear.
Social media use: She uses Google for professional use. Her favorite content is breakthrough fabric technology.
Work-related issues:
Her company is keen on adopting breakthrough fabric technology into their sportswear. She needs innovative suppliers who can constantly offer new technology solutions to differentiate their products from their competitors.
Examples of a buyer persona
Here are examples of a buyer persona.
Buyer persona for client A
Buyer persona of client B

Buyer persona of client C
Tools for creating a buyer persona
Creating a buyer persona requires a lot of time and effort. But there are some tools that help in creating a buyer persona. These include:
Tools for research
- Survey monkey to send surveys
- BuzzSumo for competitor research
- Google Analytics
- Sprout Social
- FB analytics
Tools for generating buyer persona
- Hubspot: Make my persona
- Semrush persona
- Rock Content The Ultimate Buyer persona generator
Conclusion
Buyer personas give businesses better insights into ideal customers. Businesses should use them the right way to improve their brand awareness and to market their products to attract more clients. This brand awareness will increase their sales and revenue. Also remember to update a persona as your business keeps evolving, and for those who to continue to optimize their strategy also check out this article on how to improve your business strategy with a SWOT analysis.