Using thermal energy, heating equipment can be found in many places, such as offices, homes, or residencies. Selecting the right heating equipment can be difficult because there are many machines available on the market. Nonetheless, with the right insights businesses will be able to navigate these various models to find a solution that is best for them.
This article will highlight the market potential for heating equipment, and it will discuss the different types of heating equipment available, as well as how to select the ideal machines.
Table of Contents
Market potential for heating equipment
Types of heating equipment
How to select the ideal heating equipment
Conclusion
Market potential for heating equipment
Technological advancements mainly drive the global heating equipment market. Also, some governments have initiatives to improve energy efficiency among various industries. The market is segmented by: products, such as boilers, heat pumps, furnaces, and unitary heaters; applications, such as commercial, residential, or industrial; and regionally, into North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
According to Expert Market Research, the worldwide heating equipment market was valued at USD 35.1 billion in 2020. It was forecasted to register a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% between 2021 and 2026. The increased demand for energy-efficient and cost-effective heating systems will drive growth during the forecast period.
Government initiatives like the United State’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design will result in the development of the heating equipment sector. The United States will have increased use of industrial furnaces due to the surge in industrial renovation and refurbishment. Additionally, the competitive global market has major players concentrating on reducing the general costs of the equipment. Some manufacturers include Danfoss A/S, Lennox International Inc, and Robert Bosch GmbH.
Types of heating equipment
1. Furnaces
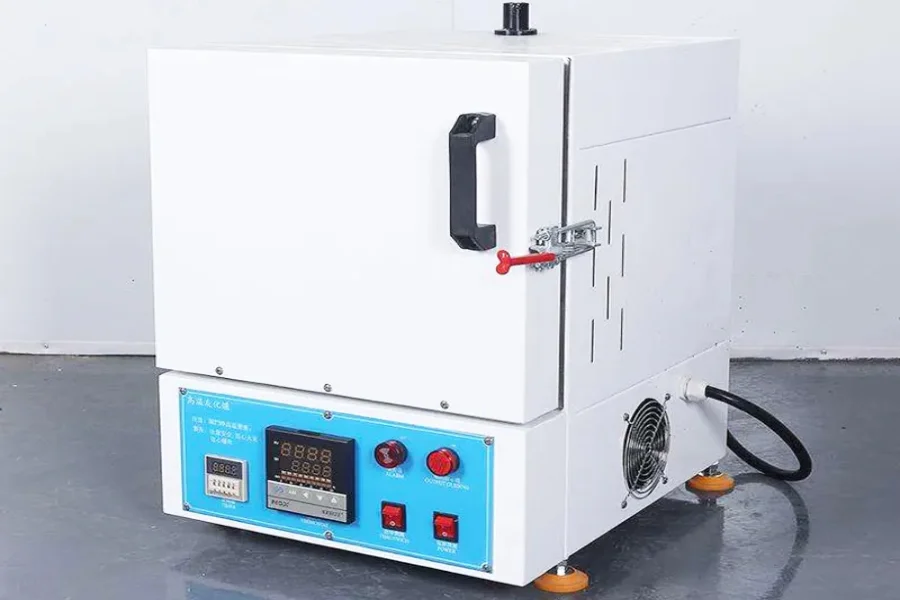

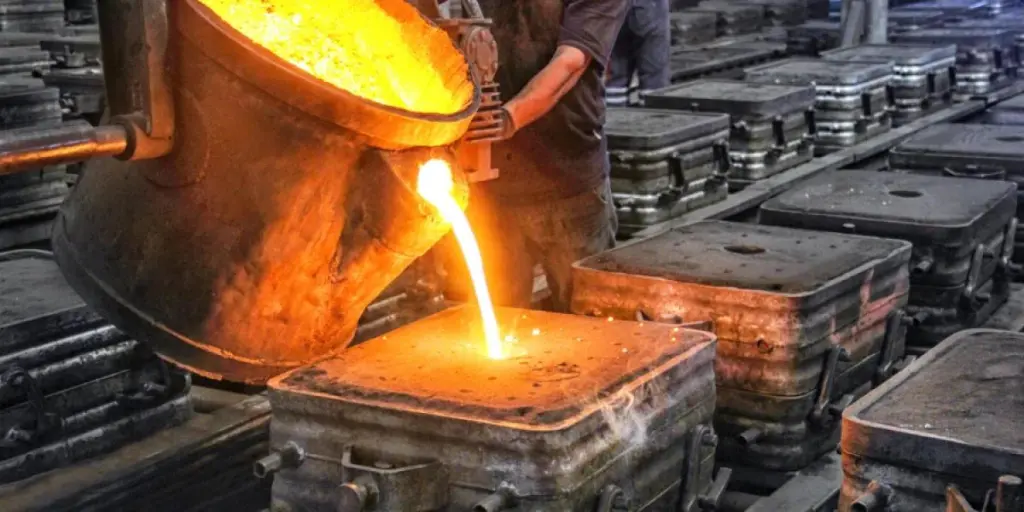
Furnaces are structures in which heat is produced through the combustion process. Examples of industrial furnaces include glass melting, solar, muffle, and vacuum furnaces. The furnaces burn fuel internally to warm air, steam, or water, and the heat is then directed to the various applications. Most furnaces burn liquid propane gas (LPG) or natural gas to generate heat. Other furnaces produce heat by burning wood, oil, or coal and through electricity. Furnaces are commonly used in factories, healthcare environments, warehouse properties, and food and beverage industries.
2. Boilers
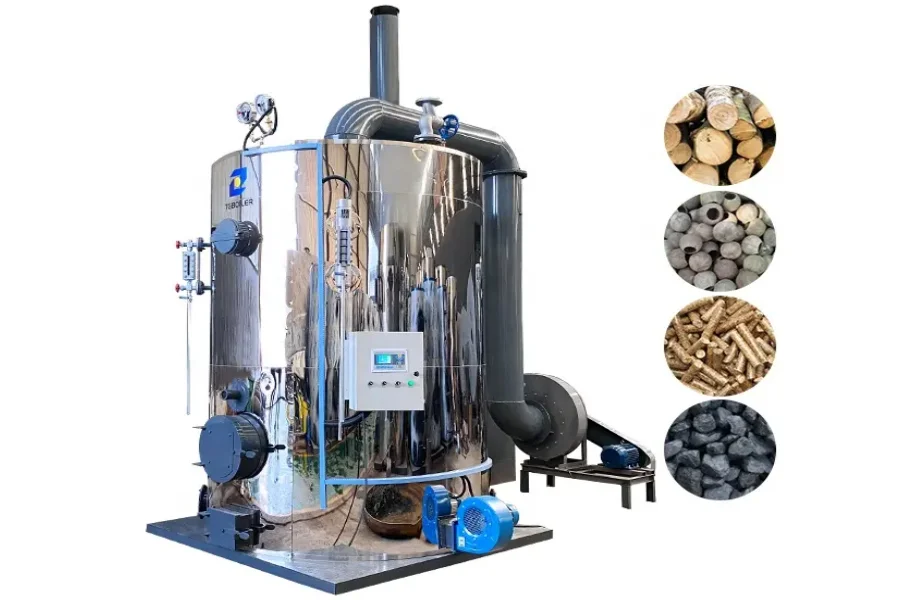

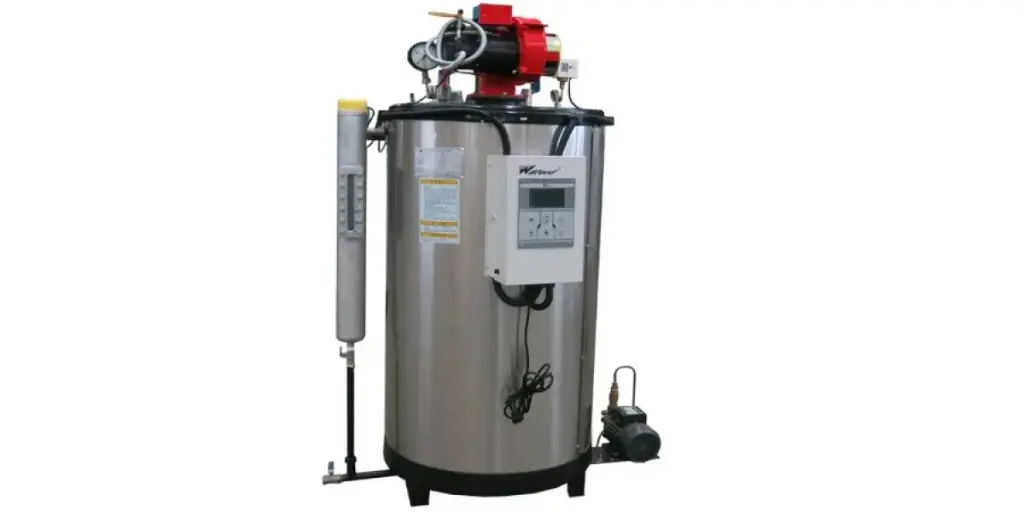
Boilers are closed vessels where fluid (water) is heated. The fluid does not have to boil, but the heated vapor exits the boilers to be used in various heating applications. These heating processes could be water heating, boiler-based power generation, central heating, sanitation, and cooking. Industrial boilers are made from thick steel, allowing extremely high pressures. Some industrial uses for boilers include production plants, restaurants and motels, multi-unit residential places, and warehouses.
3. Electric space heaters
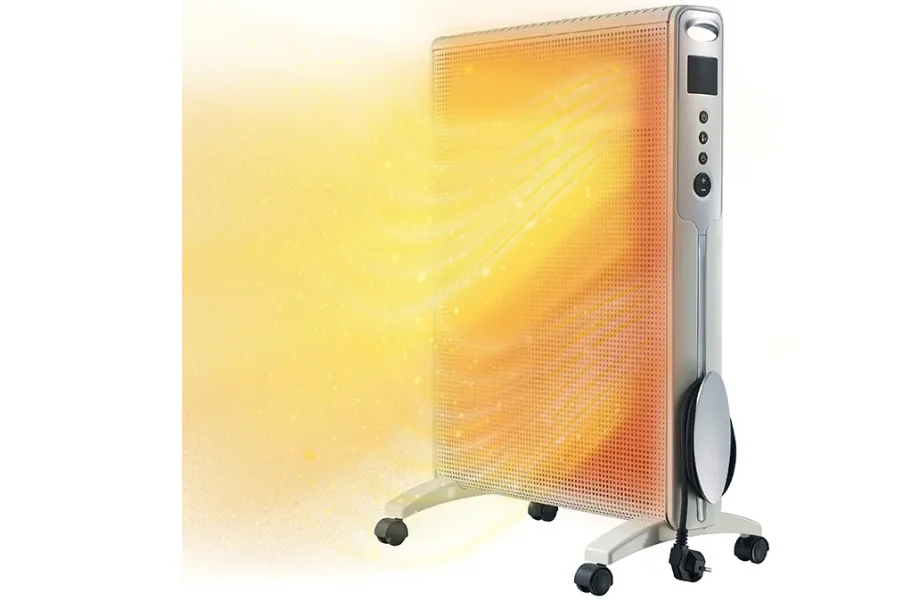

Electric space heaters are designed to focus the heat on single or small zones. The devices work by expelling hot air via a fan which naturally forces cold air to rise over the floor. This helps in the circulation of heat and in effectively warming the spaces. Electric space heaters are fast and efficient at heating rooms. In addition to manufacturing industries, electric space heaters can be applied in outdoor environments like patios, workshops, workplace buildings, garages.
4. Heat pumps
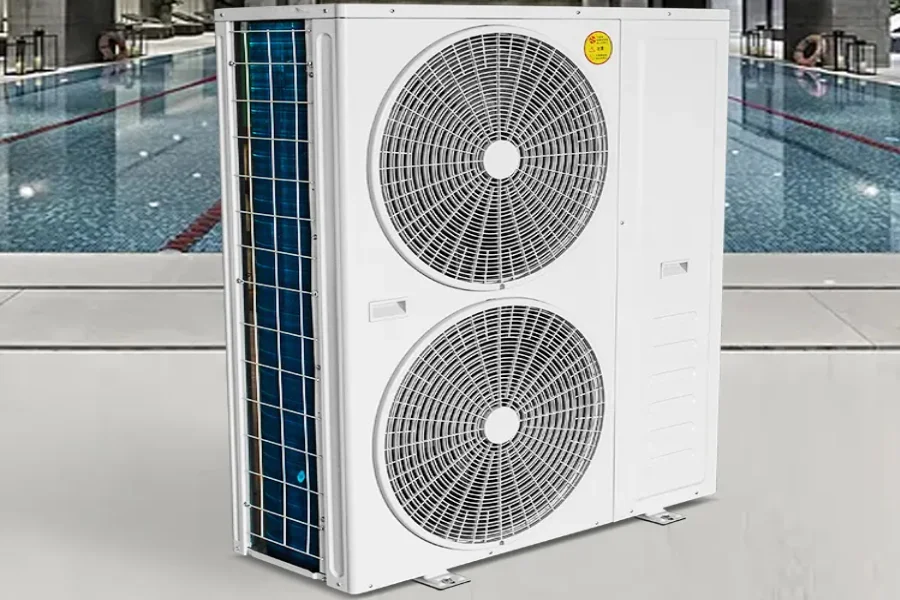

Heat pumps are electrically driven devices that extract heat from low-temperature places (source) and deliver it to high-temperature places (a sink). They efficiently provide heating, cooling, and hot water to buildings. The air and ground are the two most common heat sources for heat pumps. On the other hand, two sinks draw heat from heat pumps. They include indoor air and water inside buildings. This equipment can be used in refineries, agricultural facilities, pharmaceutical plants, and power generation facilities.
5. Gas-fired space heaters
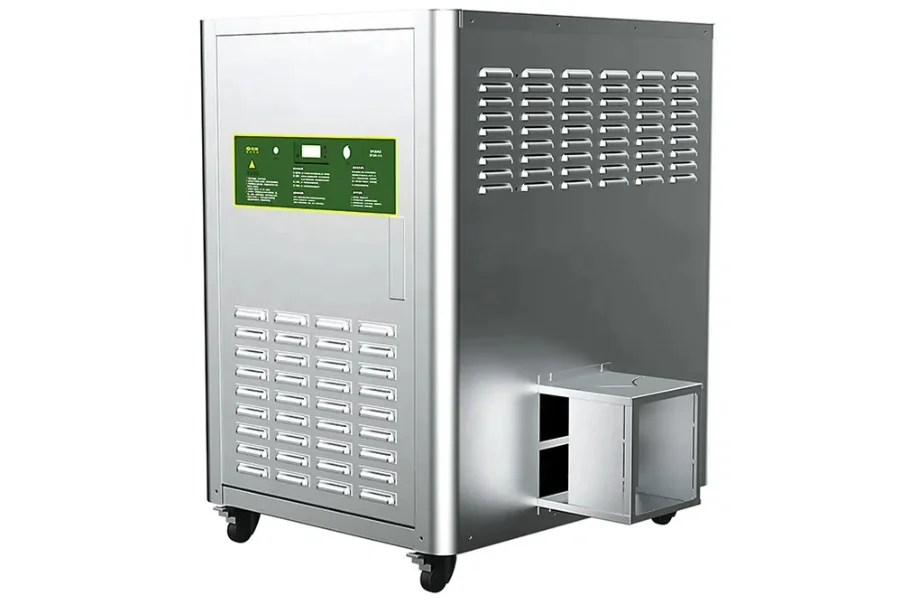

Gas-fired heaters operate by lighting several burners in a combustion chamber. The igniter sparks, or the pilot light is lit to produce heat that travels into the heat exchanger, which pushes the air through to achieve the desired temperature. Afterward, the blower sends the air out through ducts to be used in various applications like heating rooms. The burners are lit by natural gas or liquid propane gas. The equipment can be used in industrial processes like combustion, tent & event rentals, construction sites, warehouses, and manufacturing plants.
How to select the ideal heating equipment
1. Efficiency
The efficiency of heaters comes from their ability to conserve energy, thus lowering heating costs. Also, the noise level of heaters during operation determines their efficiency. For instance, the traditional furnace and boiler systems had about a 56-70% efficiency rate. In contrast, modern heating systems achieve high efficiency of about 98.5%, where they can convert nearly all fuel sources to useful heat. Notably, electric heaters are the most energy-efficient as they use less energy to produce the desired heat sufficiently.
2. Cost
Cost is an essential factor to be taken into account when purchasing heating equipment. Several factors determine the cost: initial cost, labor cost, installation cost, and maintenance cost. On average, the cost of a furnace heating system starts at around USD 3,000, depending on how powerful the system is. Buyers should consider the facility they intend to provide heat for and their allocated budget. This will greatly guide their investment decisions, where they will likely acquire the appropriate heating equipment.
3. Facility
Regarding facilities, heating equipment poses a great fire safety hazard. Buyers need to understand that heaters can cause fires if there are no adequate safety features, if they are improperly plugged in, and placed near combustibles. Facilities can be offices, homes, and industrial workplaces. These facilities require different heaters based on specific heat and safety requirements. Workplaces would require more powerful heaters than homes. Notably, heaters should be placed under windows to heat cold air from the window and avoid cold draughts on the floor.
4. Operating frequency
The choice of operating frequency for heaters is a crucial factor for heating because it essentially affects the method of heating and work to be heated. On average, furnaces with an operating frequency of about 50 Hz require a 1 MW capacity. Those with medium frequencies of about 500-1000 Hz have a 50 kW capacity, and high-frequency furnaces of 1-5 MHz have a range of capacity between 200 kW to 500 kW. Also, the temperature to be obtained affects the operating frequency, as the higher the temperature, the higher the capacity of the heater.
5. Material being heated
The materials being heated matter in selecting the appropriate heater, as it depends on whether the heating system handles gas, solids, or liquid. Considering the heater watt density control, some materials like oils or liquids that contain glucose require a lower watt density heater to circumvent burning. Likewise, gas applications require a lower watt density heater than water. Buyers should find heaters that can change the watt density to heat various materials.
6. Temperature required
The temperature requirements at which heaters operate inform the buyers of the most suitable product to acquire. Depending on the application, there are variations in the operating temperature of heaters. Primarily, the operating temperature is determined by the heating equipment’s shape, the heated materials, and the material types that comprise the heater. For instance, the ideal temperature for heaters would be between 70 to 78 degrees Fahrenheit in homes.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate heating equipment for any project or industry requires buyers to know a bit about how this equipment operates. This could be understanding heat sources and area specifications, as well as thinking through their intended outcomes. The factors mentioned here will point buyers in the right direction before they invest in a heater. To learn more, or to view listings of high-quality heating equipment, visit Alibaba.com.