1. Background of development: policy-driven 3D printing industry strengthens technological innovation
Looking at the global scale of the 3D printing industry, China ranks second in the regional structure of the global 3D printing industry, accounting for 17% due to being in the early stages of growth and lacking core technologies and cutting-edge talent. China has implemented a series of measures to promote the development of the 3D printing industry. The “Guiding Opinions on Promoting Loss Reduction and Efficiency Improvement in Agricultural Product Processing in 2021” proposes the use of new technologies such as intelligent manufacturing, biotechnology synthesis, and 3D printing to integrate and assemble a batch of high-tech content, widely applicable, and resource-saving agricultural product processing techniques and supporting equipment to reduce material and energy consumption. The “Key Points of Agricultural, Rural, Scientific, Educational, Environmental, and Energy Work in 2019,” released in 2019, proposes accelerating the research and development of intelligent agricultural technologies such as big data, cloud computing, and 3D printing to form independent innovation advantages in emerging fields.
2. Current development status: the downstream application fields are wide-ranging, and the industry market scale continues to grow
The continuous enrichment of upstream raw materials has greatly promoted the expansion of the application fields of the 3D printing industry and promoted the industry to expand from the consumer market to the high-end manufacturing market. Currently, China’s 3D printing industry application fields mainly include engineering machinery, aerospace, automotive, consumer & electronics, medical & dental, academic institutions, government & military, construction, and others. In engineering machinery, the market scale has been further expanded. Statistics show a clear upward trend in China’s 3D printing industry market scale. The market scale was only 9.8 billion RMB in 2017, and by 2021, the 3D printing market scale has reached 26.5 billion RMB, an increase of 16.7 billion RMB. It is expected to maintain a growth trend in 2022, with the market scale reaching 34.45 billion RMB.
3. Enterprise landscape: enterprise revenue is increasing, and R&D Investment is strengthening
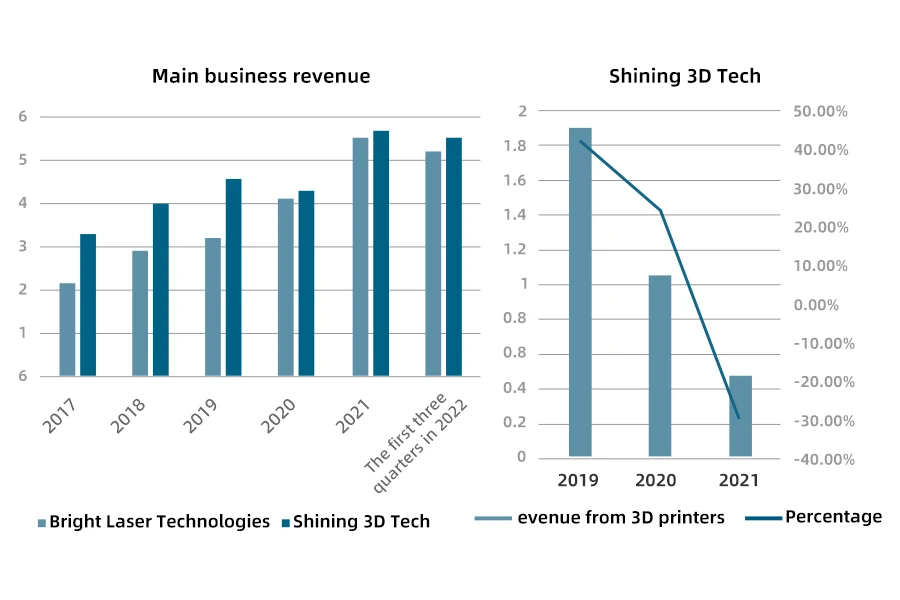
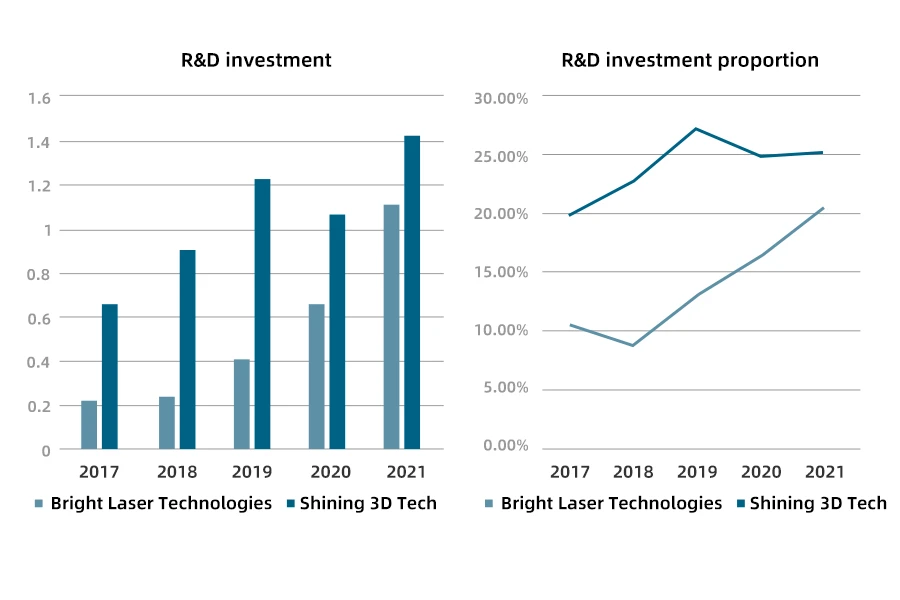
Looking at the distribution of enterprise competition levels, Bright Laser Technologies and Shining 3D Tech are in the second tier, with operating income exceeding 500 million RMB. In the first three quarters of 2022, Bright’s total operating income was 520 million RMB, and Shining 3D’s main business income reached 548 million RMB. Bright is a high-tech enterprise specializing in industrial metal additive manufacturing. Its main operating income is in the 3D industry products, and its R&D investment also shows an increasing trend. By 2021, the company’s R&D investment reached 114 million RMB, accounting for 20.69% of total operating income. Shining 3D is a technology innovation enterprise specializing in high-precision 3D digital software and hardware technology based on computer vision. 3D printing is one of its products, and in 2021, the 3D printing product’s operating income accounted for about 8% of total operating income. The company’s R&D investment was 144 million RMB, accounting for 25.37% of total operating income.
4. Development trends: the application fields of the 3D industry continue to expand, and sustainable development is a top priority for the industry
In the future, the global 3D printing industry will still be in high growth. As China continues to break through technological barriers, the industry will continue to grow and enter a period of large-scale industrialization. There is a strong demand for metal 3D printing in the aerospace, automotive, marine, nuclear, and medical equipment industries, and the application end is showing a rapid expansion trend. As the country gradually attaches importance to environmental protection, industry development is gradually changing to comply with policy trends. Engineers and designers will rethink the design throughout the entire life cycle of the product to achieve the integration of the structure of the parts, reduce material consumption and waste by producing lightweight parts with complex geometric shapes, further reduce the weight of vehicles and aircraft, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. Moreover, as more and more manufacturers transfer digital files for local production rather than delivering goods through transportation from distant places, transportation will be greatly reduced, further reducing costs, energy consumption, waste, and emissions.
Keywords: 3D printing; Application fields; Enterprise landscape; Development trends
1. Background of development: policy-driven 3D printing industry strengthens technological innovation
Looking at the global scale of the 3D printing industry, the global 3D printing market scale reached 15.244 billion USD in 2021. The United States accounted for 40% of the global share, making it the main concentration area for current 3D printing companies. China’s 3D printing industry is in the early stages of growth, and the lack of related core technologies and cutting-edge talent severely restricts the development of China’s current 3D printing industry. China ranks second in the regional structure of the global 3D printing industry in terms of market share, accounting for 17%.
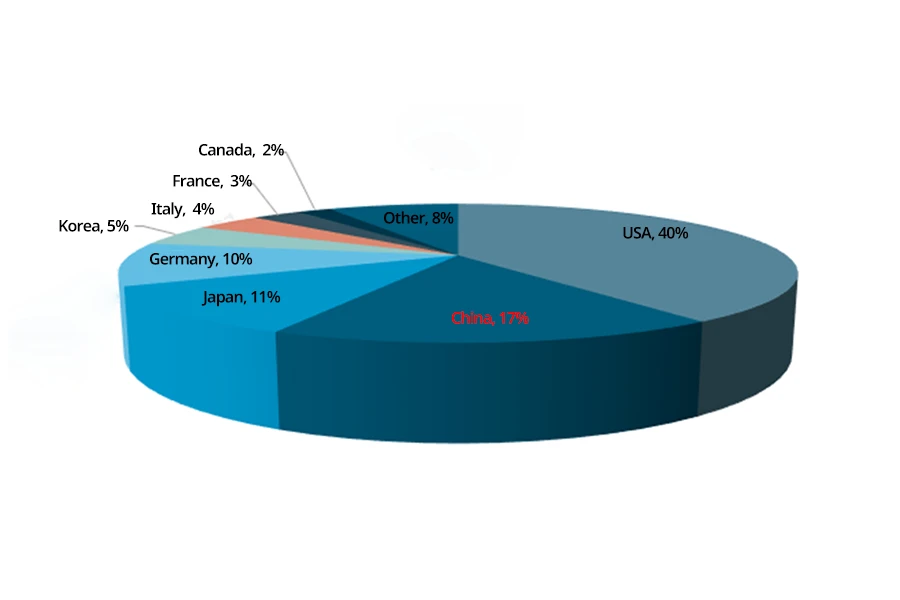
Under the wave of global digital manufacturing, intelligent robots, artificial intelligence, and 3D printing technology are continuously developing. Although China’s 3D printing technology has some shortcomings, and the industry is still immature, it has demonstrated its unique advantages in product design, production of complex and special products, and personalized services. Therefore, China fully recognizes the profound impact of intelligent manufacturing and digital manufacturing on the country, accelerates the development of the 3D printing industry, and promotes China’s transformation from a “manufacturing power” to a “manufacturing powerhouse.” The “Guiding Opinions on Promoting Loss Reduction and Efficiency Improvement in Agricultural Product Processing in 2021” proposed the use of new technologies such as intelligent manufacturing, biotechnology synthesis, and 3D printing to integrate and assemble a batch of high-tech content, widely applicable, and resource-saving agricultural product processing techniques and supporting equipment to reduce material and energy consumption. In the “Overall Plan for Shanghai’s Comprehensive Pilot Program for Expanding Service Industry Opening-Up,” the Chinese government strengthens the function of national digital service export bases. It encourages the development of leading industries such as integrated circuits, digital culture, artificial intelligence, and information security. It also actively lays out emerging fields such as 3D printing and big data and accelerates the concentration of a group of digital service enterprises with global influence. The “Key Points of Agricultural, Rural, Scientific, Educational, Environmental, and Energy Work in 2019,” released in 2019, proposed accelerating the research and development of intelligent agricultural technologies such as big data, cloud computing, and 3D printing to form independent innovation advantages in emerging fields.
2. Current development status: the downstream application fields are wide-ranging, and the industry market scale continues to grow
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a type of rapid prototyping technology that uses digital model files to construct objects through layer-by-layer printing using materials that can be bonded, such as powder metal or plastic. Looking at the industrial chain of the 3D printing industry, the upstream industry mainly includes raw materials, core hardware, auxiliary tools, and so on; the middle industry mainly includes equipment manufacturers and 3D printing service providers; the downstream industry is mainly applied to machinery manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, medical, education, military, culture, and so on, with special applications including biotechnology, food, architecture, and portrait printing, among others.
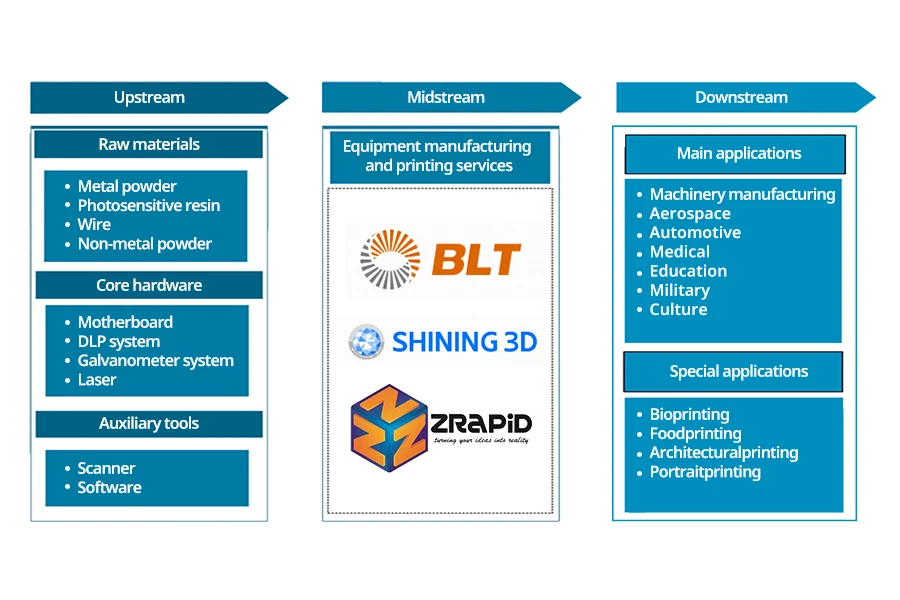
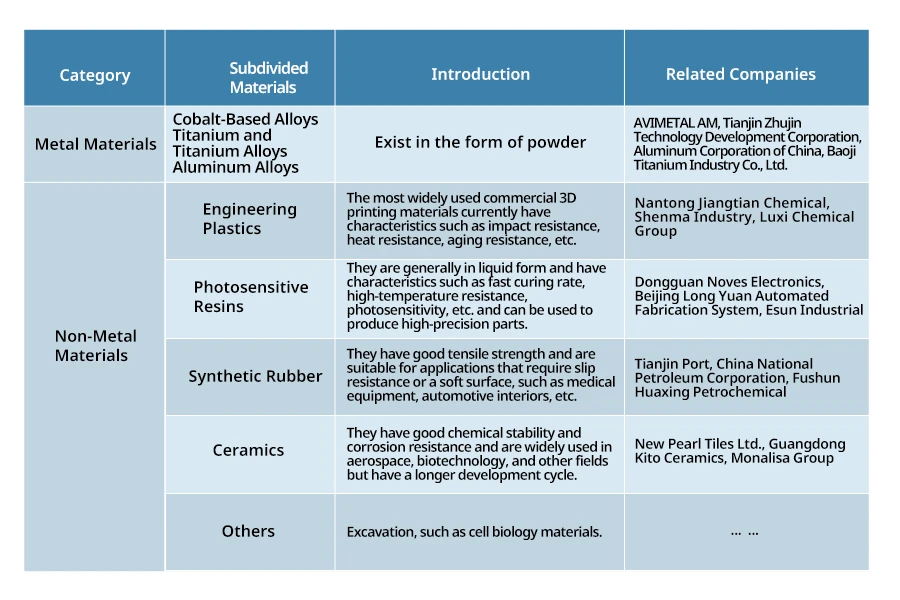
3D printing materials are a midstream component supporting the 3D printing industry. According to statistics, 3D printing materials are mainly divided into metal and non-metal materials. Metal materials are mainly powder, while non-metal applications are relatively extensive, including engineering plastics, photosensitive resins, synthetic rubber, ceramics, and other non-metal materials. Engineering plastics are the most widely used 3D printing materials with features such as impact resistance, heat resistance, and aging resistance. Liquid photosensitive resin has a fast-curing rate, high-temperature resistance, and photosensitivity, making it widely used to produce high-precision parts. Synthetic rubber has good tensile strength and is mainly suitable for medical equipment, automotive interiors, and other fields. Ceramics have good chemical stability and strong corrosion resistance and are widely used in the aerospace and biotechnology industries.
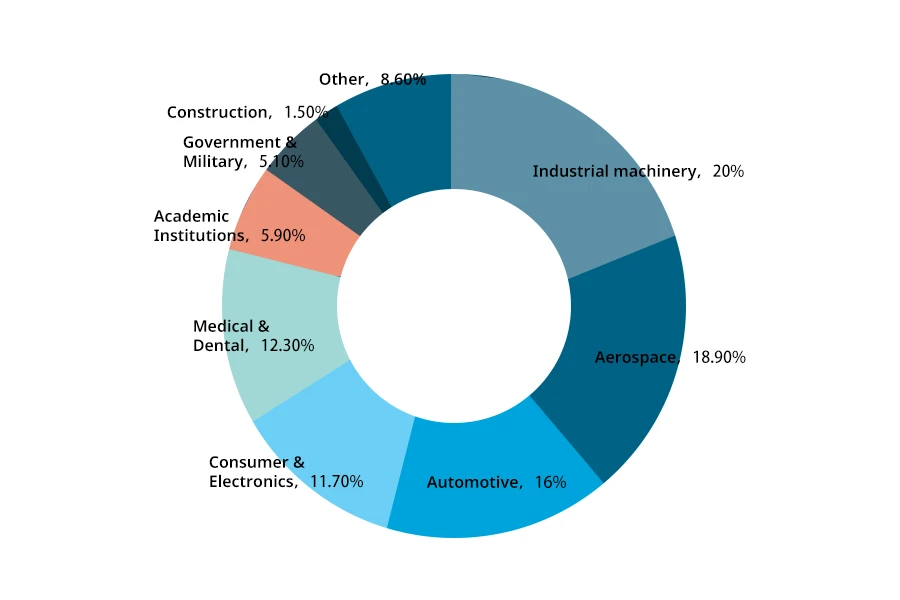
With the continuous enrichment of upstream raw materials, the 3D printing industry has greatly expanded its application areas, promoting its expansion from consumer to high-end manufacturing markets. Currently, the application areas of China’s 3D printing industry mainly include engineering machinery, aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics, medical and dental, academic institutions, government and military, construction, and others. In engineering machinery, the application of 3D printing technology mainly includes additive manufacturing technology, integration with CNC technology, and changing the pattern of machinery manufacturing, which plays an important role in improving overall production efficiency and reducing production costs. In aerospace, 3D printing technology can quickly manufacture complex parts and repair existing ones. 3D printing technology can be applied to developing automotive exterior design in the automotive field. It can print out models quickly and quickly produce complex-shaped parts and customized components in small batches.
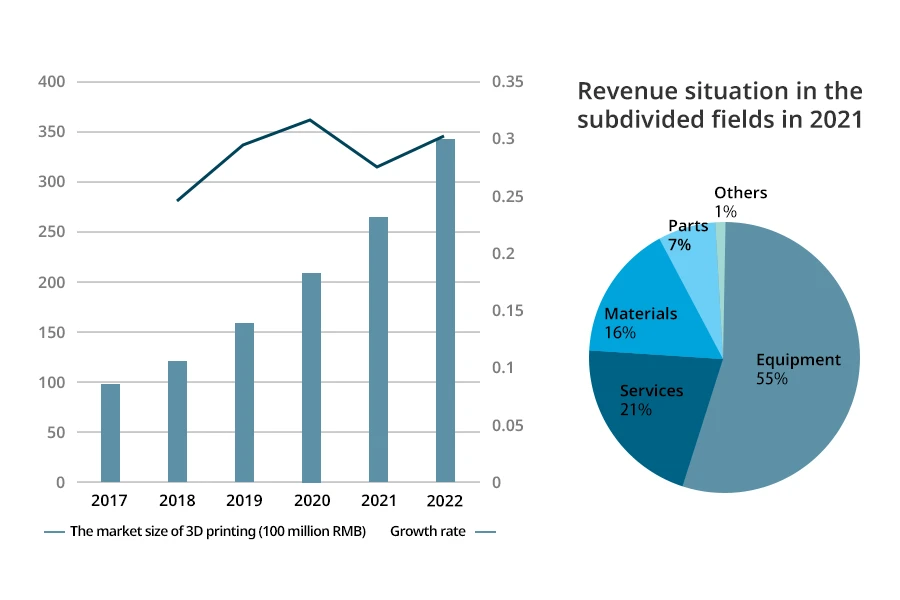
The development of 3D printing technology has been continuously improved under the influence of policies, coupled with the rapid development of downstream industries, resulting in a surge in demand for 3D printing equipment and further expanding the industry’s market size. According to statistics, the market size of China’s 3D printing industry has shown a clear upward trend. In 2017, the market size was only 9.8 billion RMB, but by 2021, the 3D printing market size had reached 26.5 billion RMB, an increase of 16.7 billion RMB. It is expected to grow in 2022, and the market size is expected to reach 34.45 billion RMB. In terms of revenue in the subdivided fields in 2021, the revenue of 3D printing equipment accounted for more than 50%, ranking first. It can be seen that equipment is the main part of the 3D printing industry. Secondly, the revenue from 3D printing services accounted for 21%, and materials revenue accounted for 16%.
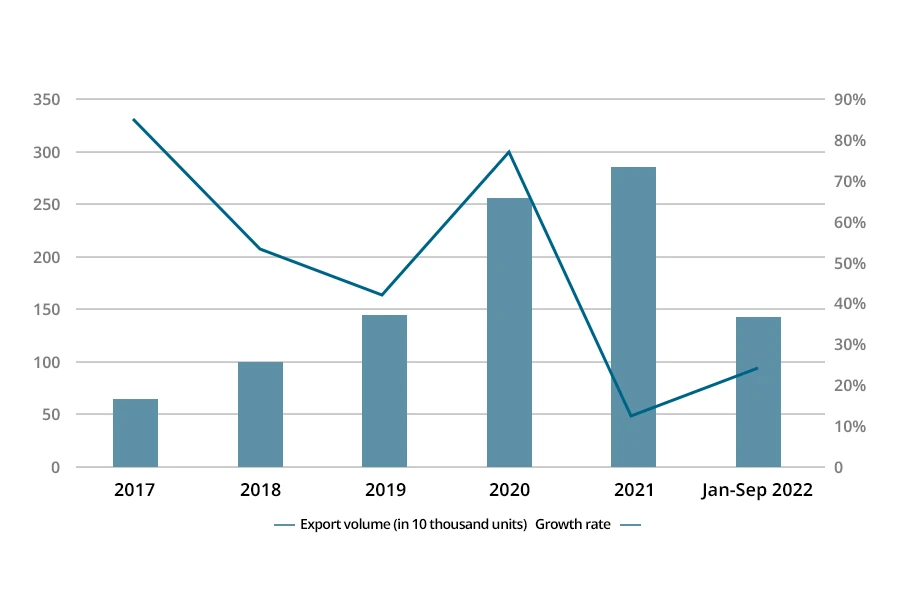
With the continuous promotion and popularization of 3D printing technology, the sales of 3D printing devices for personal consumption are growing rapidly. According to China Customs data, the number of 3D printers exported from China in 2021 was 2.873 million units, an increase of 13% compared to 2020; the export volume in the first three quarters of 2022 was 1.452 million units, an increase of 25% compared to the same period in 2021. Looking at the data from recent years, the number of 3D printers exported from China has been continuously increasing. From 2017 to 2020, the export volume increased from 656,000 units to 2.539 million units. As the base continues to grow, the growth rate decreased from 85% in 2017 to 42% in 2019, then increased to 77% in 2020.
With the continuous support of national policies, the 3D printing industry has achieved sustained development, which has promoted the increase of patent applications in the 3D printing industry. Looking at the number of 3D printing patent applications from 2017 to 2020, the number of 3D printing patent applications in China continued to rise, from 5,718 in 2017 to 7,501 in 2020. However, the number of patent applications gradually declined in 2021, reaching 6,618, a decrease of 12% compared to 2020. In 2022, the number of patent applications was also in a downward trend, with a total of 3,597, a decrease of 3,021 compared to the whole year of 2021.
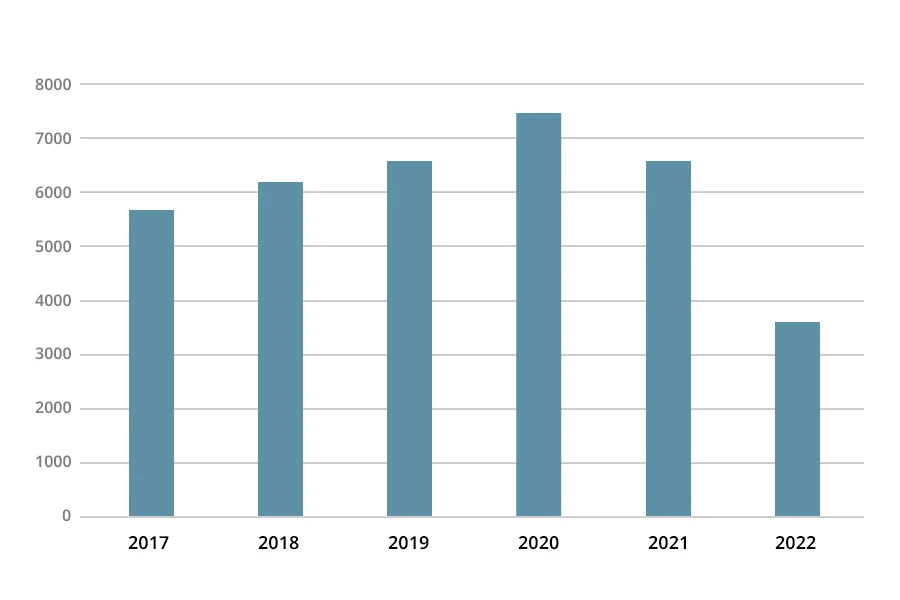
Note: The data for 2022 is up to December 7, 2022.
3. Enterprise landscape: enterprise revenue is increasing, and R&D investment is strengthening
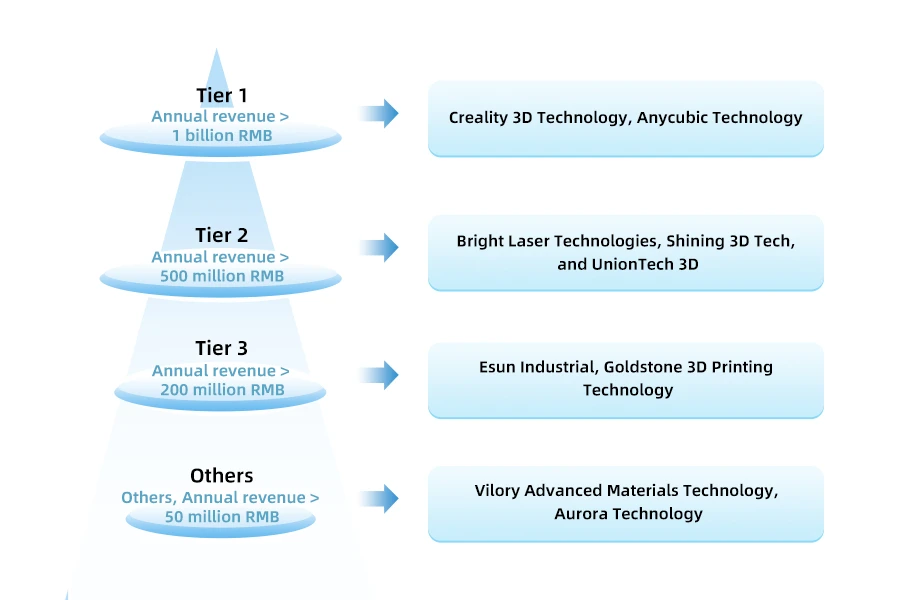
In 2021, there were 50 companies in the Chinese 3D printing industry with annual revenue exceeding 100 million RMB. The total annual revenue of these 50 companies was about 11 billion RMB, compared to only 32 companies with revenue exceeding 100 million RMB in 2020, an increase of 56% year-on-year. Regarding the distribution of competition levels among companies, Creality 3D Technology, and Anycubic Technology are in the first tier, with annual revenues exceeding 1 billion RMB. The second tier includes Bright Laser Technologies, Shining 3D Tech, and UnionTech 3D, with annual revenues exceeding 500 million RMB. The third tier includes Esun Industrial and Goldstone 3D Printing Technology, with annual revenues exceeding 200 million RMB. It can be seen that the difference in revenue between the top companies and the second and third tiers is not significant. Vilory Advanced Materials Technology and Aurora Technology are in the fourth tier, with annual revenues exceeding 50 million RMB.
Bright is a high-tech enterprise focused on industrial-grade metal additive manufacturing and is at the forefront of the metal additive manufacturing field both domestically and internationally. The company conducts research and development, production, and sales of metal 3D printing equipment, customized products, and metal 3D printing raw materials around the metal additive manufacturing industry chain. It also provides customers with metal 3D printing process design and development and related technical services. Looking at the company’s total revenue from 2017 to 2021, Bright’s revenue increased from 220 million RMB in 2017 to 552 million RMB in 2021. In the first three quarters of 2022, the company’s total revenue was 520 million RMB. Shining 3D Tech is a technological innovation enterprise focusing on high-precision 3D digital software and hardware technology based on computer vision. It mainly researches, develops, produces, and sells dental digitalization and professional 3D scanning equipment and software. The total revenue of Shining 3D Tech was on an upward trend from 2017 to 2021. However, due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the main business revenue declined in 2020 but gradually increased to 567 million RMB in 2021. In the first three quarters of 2022, the company’s main business revenue reached 548 million RMB. In terms of 3D printing, dental 3D printers are digital products independently developed by the company, and its revenue decreased from 190 million RMB in 2019 to 46 million RMB in 2021.
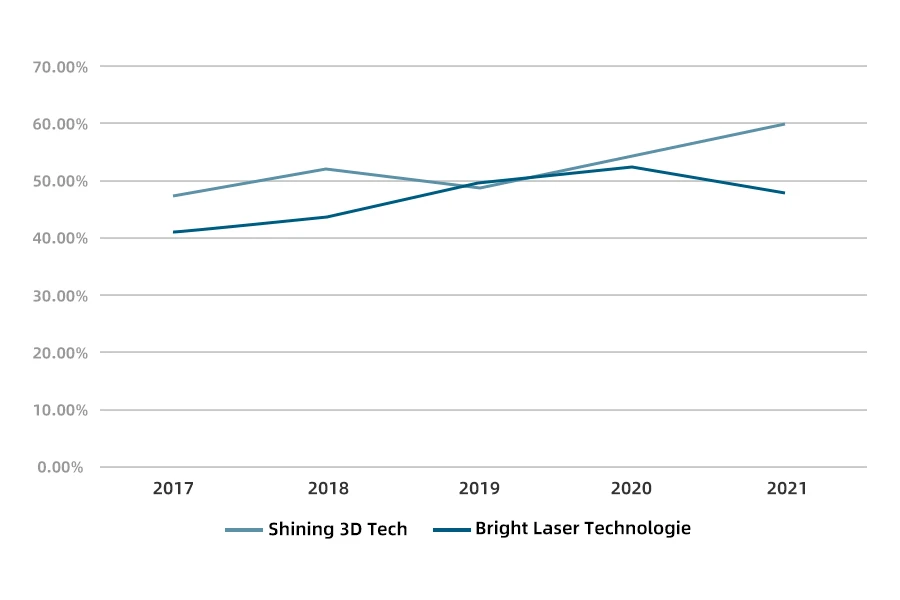
Looking at the gross profit margin of companies, Bright and Shining 3D have both shown an overall upward trend in gross profit margin. Among them, Bright’s gross profit margin increased from 2017 to 2020, reaching its highest point in recent years at 52.72% in 2020 before gradually declining to 48.23% in 2021. Shining 3D’s gross profit margin decreased from 51.98% in 2018 to 49.17% in 2019 and gradually increased. By 2021, Shining 3D’s gross profit margin had increased to 59.87%, a 10.20% increase from 2020.
Looking at the R&D investment of companies, Bright adheres to the strategic direction of integration of industry, academia, and research and currently has significant advantages in multiple areas of competition. From 2017 to 2021, Bright’s R&D investment has been in a state of continuous growth. In 2021, the company’s R&D investment reached 114 million RMB, accounting for 20.69% of its total revenue. Shining 3D can improve the extensibility and stability of 3D printing equipment through independent research and development, which is conducive to the improvement of subsequent R&D capabilities, and facilitates the docking of upstream and downstream raw materials and software as software and product upgrades. Its R&D investment declined in 2020 due to the impact of the pandemic but increased to 144 million RMB in 2021, accounting for 25.37% of its total revenue.
4. Development trends: the application fields of the 3D industry continue to expand, and sustainable development is a top priority for the industry
4.1 The demand continues to expand, and the future development potential of the 3D printing industry is enormous
As we all know, technological innovation is vital in developing various industries, including the 3D printing industry. With the global development and promotion of 3D technology, the demand for 3D printing materials continues to increase. The unique nature of 3D printing technology and its dependence on materials has led to an increasing number of market participants in the 3D printing materials industry and increased industry profits. The technological barriers to 3D printing materials are expected to increase further, indicating that the industry still needs to increase research and development investment to expand the application areas of 3D printing. The global 3D printing industry is expected to continue to grow rapidly in the next decade, and China’s industry will continue to grow and enter a large-scale industrialization phase as it continually breaks through technological barriers. There is a strong demand for metal 3D printing in industries such as aerospace, automotive, shipping, nuclear industry, and medical equipment, and the application end is showing a rapid expansion trend. In the future, the application of 3D printing technology will move from simple concept models to directly manufacturing functional parts, and the industry’s development potential is enormous.
4.2 Sustainable production is an important development direction for the 3D printing industry
The country has gradually attached great importance to environmental protection in recent years, and the industry has gradually changed to comply with the policy trend. Previously, traditional manufacturing processes rarely considered environmental issues during design, and about one-third of carbon emissions were related to product production and logistics. However, 3D printing can effectively reduce the waste, carbon dioxide, and other emissions the manufacturing industry produces. Coupled with the current launch of lightweight, it is beneficial for applying the 3D industry in areas such as automobiles and aircraft. Engineers and designers will rethink the design throughout the entire product lifecycle to achieve structural integration of the parts. By producing lightweight parts with complex geometries, they can reduce material consumption and waste, reduce the weight of vehicles and aircraft, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and energy consumption. Moreover, as more and more manufacturers transmit digital files for local production rather than delivering goods through long-distance transportation, transportation will be greatly reduced, further reducing costs, energy consumption, waste, and emissions.
Source from Intelligence Research Group (chyxx.com)




