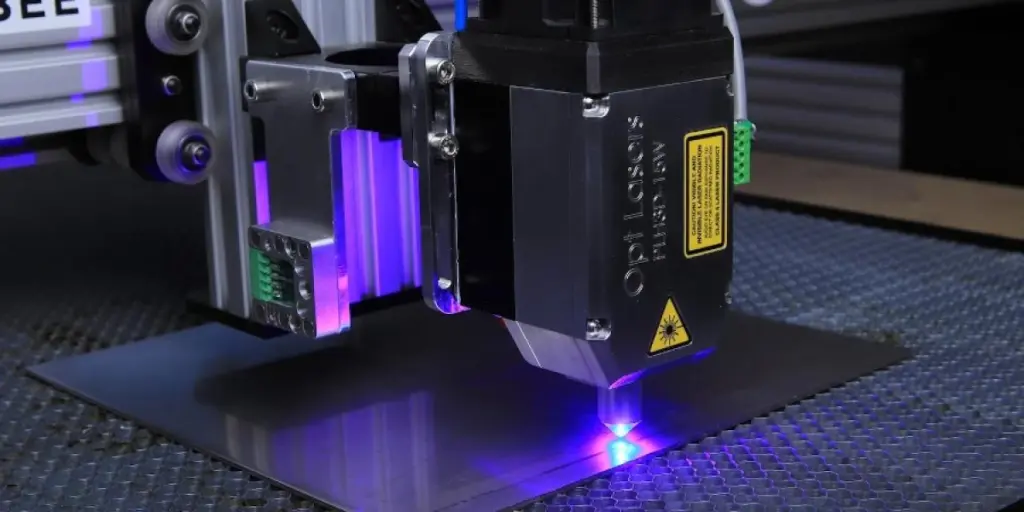
Thanks to technological advancement, modern engraving machines can engrave any material with great speed and accuracy. However, for deep metal engraving, even a standard fiber laser will not suffice because it necessitates a machine with specialized capabilities. Continue reading to learn what characteristics to look for when purchasing metal engraving machines.
Table of Contents
Overview of the laser engraving machine market
What is metal engraving?
Factors to consider when buying a metal engraving machine
Conclusion
Overview of the laser engraving machine market

The global laser engraving machine market was valued at US $3.5 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% to reach US $6.19 billion by 2028.
In the future, the Asia-Pacific region will account for most of the market share, with China accounting for nearly 30% of total sales. The US is also expected to be a significant growth market, owing to the growing popularity of custom engraved products among American consumers.
Fiber laser engraving machines are the most popular option accounting for 45% of market shares, followed by CO2 lasers, accounting for 30% of total sales. The growth can be attributed to the increasing demand for engraving machines across the automobile, advertising, and education industries. Furthermore, the introduction of 3D engraving systems will boost the demand in the future.
What is metal engraving?
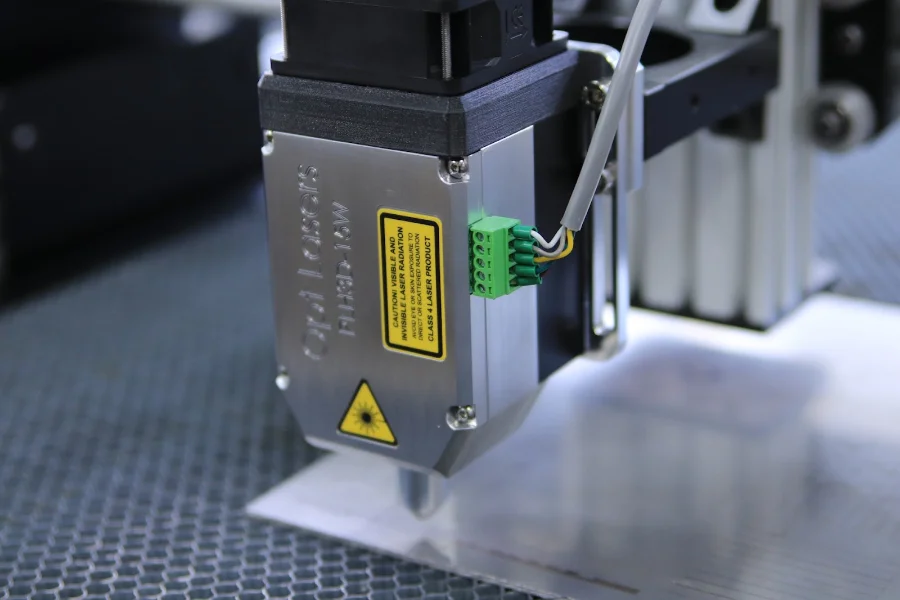

Metal engraving is a method of permanently imprinting text, logos, and numbers on a surface. It is done with the help of laser technology, in which a laser beam is directed onto a surface, heating, melting, and vaporizing the area where the laser beam is aimed.
Modern machines can work with most metals commonly used in manufacturing, including black, non-ferrous, and noble metals. Gold, silver, steel, bronze, aluminum, brass, and platinum are the best metals for engraving. The metal’s properties determine the right type of equipment and the required laser source and power. Metals with a high reflectivity necessitate stronger emitters.
What are the different types of laser engravers?
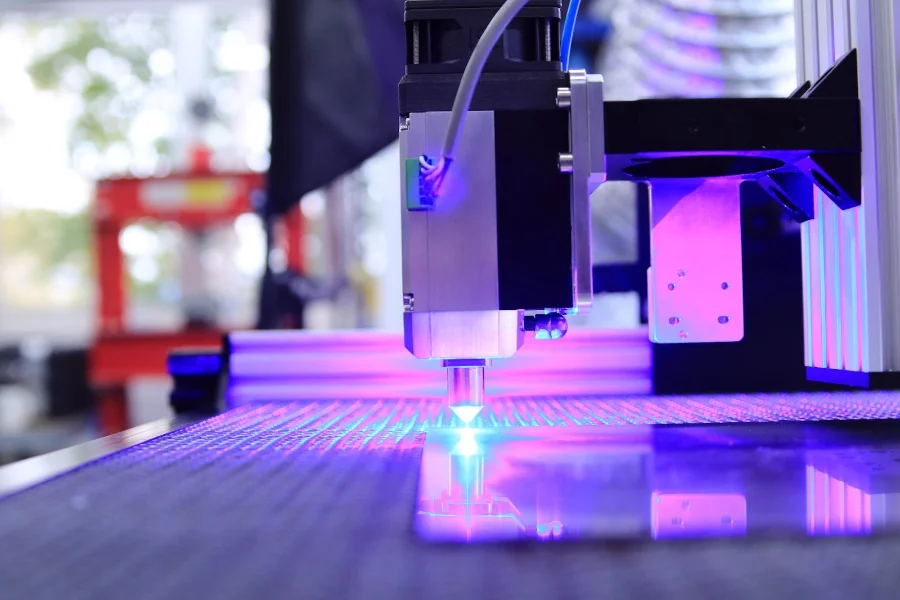
CO2 lasers: This is the most common type of gas laser that emits infrared radiation and has a wavelength of approximately 10.6 nm, making it the most powerful laser available. High-powered CO2 lasers are used in various industrial applications, while low-power options are used for engraving small details on commodities.
Fiber lasers: They have a wavelength of 1.064 nm and a shorter focal length, but are ten times more powerful than CO2 lasers. They are widely used to permanently mark metals with barcodes, ID codes, and serial numbers because they are ideal for metal processing. Additionally, fiber lasers produce better beams, and the laser beam can be adjusted to alter the surface color of the material to create unique decorative effects.
Factors to consider when buying a metal engraving machine

1. Emitting power
For the machine to engrave things deeply enough, a high-powered laser is required. If the machine is subjected to excessive strain, it may succumb to wear and tear. As a result, before settling on a model, one must determine the required depth for their markings. A 20W or 30W engraving machine is ideal for permanent markings. If there are special requirements, a fiber laser with a power output of 50W or 60W is the best option.
Users can adjust for different factors, such as beam expansion, mode structure, resonator set-up, and focal point, if they are aware of the depth of the marking. The engraving tolerance is also affected by the rate of removal. Some machines may have a higher removal rate but poor accuracy.
Individuals seeking pinpoint accuracy should look for machines with extra features, such as a laser measuring tool or a mechanical probe. Although they are more expensive, they will ensure higher precision and quality.
2. Laser source
The laser power source converts electrical energy into laser power for engraving. Low-quality laser engravers may have a weak laser source, occasionally resulting in inaccurate engravings. Knowing the laser source and wavelength allows one to determine whether a particular machine is appropriate for their needs.
A fiber laser with a wavelength of 1,064 nm is ideal for processing metals. A thulium-doped fiber laser with a wavelength of 1,040 nm is best suited for engraving medical equipment. The erbium-doped fiber laser of a wavelength of 1,550 nm is great for telecommunication purposes. Thus fiber lasers operate at different wavelengths for different requirements, and one must look up the laser source to understand its potential.
3. Laser beam output
Consider whether the laser beam is continuous or pulsed when shopping for an industrial laser engraving machine. Continuous-wave laser beams have consistent energy levels, making them ideal for laser drilling, welding, and cutting machines.
Pulsed laser beams have high energy peaks, making them ideal for engraving permanent markings or piercing holes without melting the surrounding material. Nevertheless, some machines can change modes.
4. Material
One of the most important factors to consider is the material one will use. Some materials are easier to engrave than others and thus may not require the same features from machines as more complex materials. For example, aluminum and brass are easier to engrave than titanium and steel. But just as steel will affect the average power requirements of the laser, so will alloys like brass and copper.
It is necessary to consider the physical properties of the metals and the final product. The configurations of the laser engraver will be influenced by factors such as cycle time, workpiece fixturing, loading/unloading, weight, and size. Before purchasing a laser engraving machine, it is critical to understand the properties of the materials.
5. Table size
The table size determines the size of the material that can be engraved in the machine. A larger table accommodates larger pieces of material and allows users to engrave multiple items with jigs in one run. Although some models can be expanded with add-ons to create a larger workspace, most models have a fixed size.
6. Throughput
A laser engraving machine with a high working speed will ensure faster results, saving time. A laser machine with a large table size should have a matching speed, or the project may take a long time to complete.
As a result, choosing a machine with a higher wattage is a good idea because it is directly related to speed. Although higher watts are not required for materials such as plastic and acrylic, more complex materials such as wood and stone will need high speed to achieve the best results.
7. Technology
It is wise to opt for machines equipped with the latest technology. This is because they are compatible with a wide range of accessories, giving users a host of new functionalities. For instance, metal engraving tools like 3D galvanometer heads for fiber lasers is a new technology that can be affixed to the latest machines.
This add-on allows the machine to make engravings on uneven surfaces, make deep engravings easily, and adjust the laser focus.
Other features to consider are laser safety per CDRH regulations, capacity to remove waste such as smoke, splatter, and dross, fume extraction, and facility considerations such as machine size and environmental factors.
Conclusion
Metal engraving machines are expensive, and searching for a deep laser engraver is a complex task. One must carefully weigh all available information before purchasing to avoid costly errors.
This article discussed several significant factors, including laser power, laser source, technology, and materials, and why it is crucial to consider them. Visit Alibaba.com to explore the leading metal engravers available today.